Catalog
Empowering users to find the right data
The Catalog feature is designed to help users efficiently locate and explore data within Amorphic. It provides a comprehensive global metadata search capability, enabling rapid and precise identification of data assets.
Key Benefits:
- Efficient Data Discovery: Quickly find and explore data assets.
- Comprehensive Search: Search across all available data to pinpoint exactly what's needed.
- Metadata Exploration: Facilitates rapid and precise identification of data assets using global metadata search.
Getting Started
Accessing Catalog
Users can access and explore the catalog under the Data Discovery section: Data Discovery → Catalog.
Search Types
There are two types of search techniques supported in Catalog:
-
Keyword Search: The search operates primarily on metadata, including explicit keywords assigned during resource creation, as well as dataset names, descriptions, and other metadata fields to quickly surface matching results. Keyword search is case-insensitive, so you don't need to worry about matching the exact case of asset names or keywords when entering your query.
-
Semantic Search: An AI-driven search functionality that understands the intent and meaning behind your query, not just exact keyword matches. Instead of searching for specific words, semantic search uses natural language understanding to find resources that are conceptually related to what you're looking for.
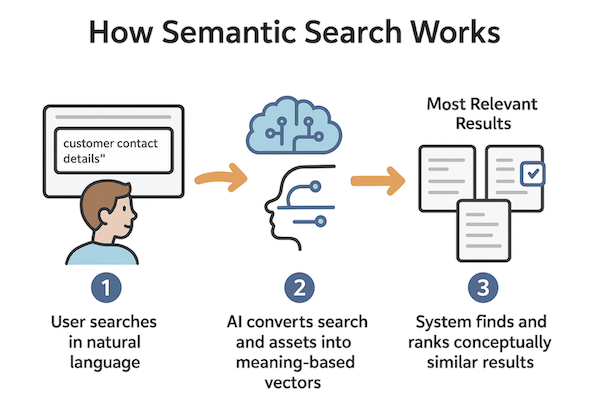
Keyword Search vs. Semantic Search: A Comparison
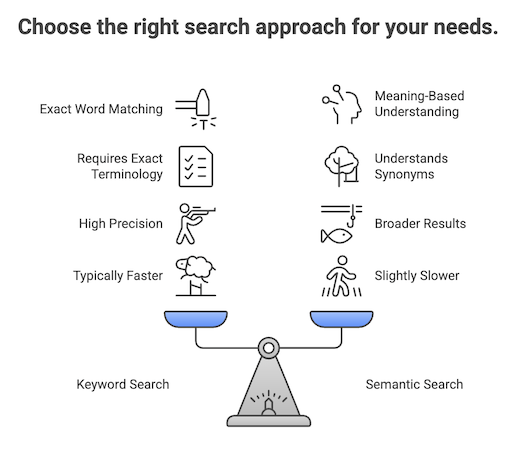
Understanding the differences between keyword and semantic search helps you choose the right approach for your needs:
-
Matching: Keyword search performs exact word and phrase matching, requiring your query terms to appear literally in the asset metadata. Semantic search, on the other hand, uses AI-powered natural language understanding to interpret the meaning and context behind your query, matching concepts rather than specific words.
-
Flexibility: Keyword search requires you to use the exact terminology that appears in asset names, descriptions, or keywords. If you don't know the precise terms used, you might miss relevant assets. Semantic search is more flexible—it recognizes synonyms, related concepts, and alternative phrasing. For example, searching for "revenue" will also find assets labeled as "income" or "sales."
-
Precision: Keyword search provides highly precise results when you know the exact terms to search for, making it ideal for finding specific assets by name or known keywords. Semantic search prioritizes intent over exact matches, returning results that conceptually align with what you're looking for, which can include related assets you might not have considered.
-
Speed: Keyword search typically returns results more quickly since it performs straightforward text matching without additional processing overhead. Semantic search involves AI model processing to generate embeddings and perform similarity calculations, which may add a small delay, though the difference is usually minimal for most users.
-
Use Case: Choose keyword search when you need to find specific assets by their exact names or when you know the precise metadata terms used in your organization. This approach is best for targeted searches where precision is critical. Use semantic search when you're exploring data assets, discovering related concepts, or unsure of the exact terminology your organization uses. It's ideal for exploratory searches and finding assets that relate to your query conceptually.
To get the most accurate and relevant results from semantic search, follow these recommendations:
-
Provide Detailed Asset Descriptions: When creating or updating assets, include comprehensive descriptions that clearly explain the asset's purpose, content, and context. Well-described assets are more likely to be matched accurately by semantic search queries.
-
Use Multiple Keywords in Your Query: Include as many relevant keywords as possible in your search query to help narrow down the results.
-
Semantic search analyzes asset descriptions, names, keywords, and other metadata fields. If any of these fields semantically match your query, the asset will be returned in the results.
-
You may notice some results that seem less relevant. This typically occurs when assets have minimal descriptive information—without sufficient context in the asset's description, name, or keywords, the system may not be able to differentiate between relevant and non-relevant results as precisely.
Pre-requisites for using Semantic search:
- Semantic search is available only in AI-enabled environments.
- Further, you need to enable Catalog within the Manage AI Services section of AI Space within Amorphic.
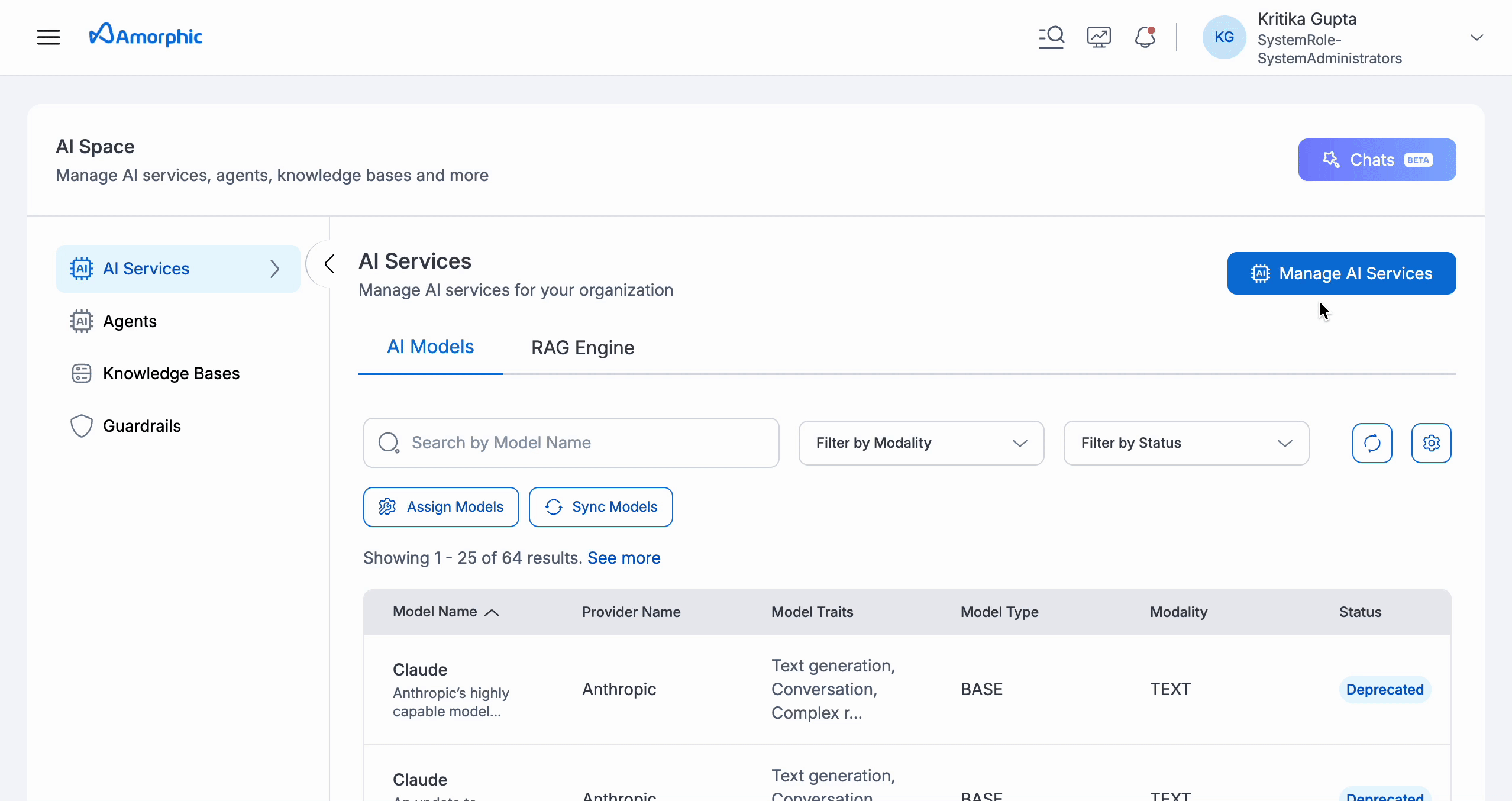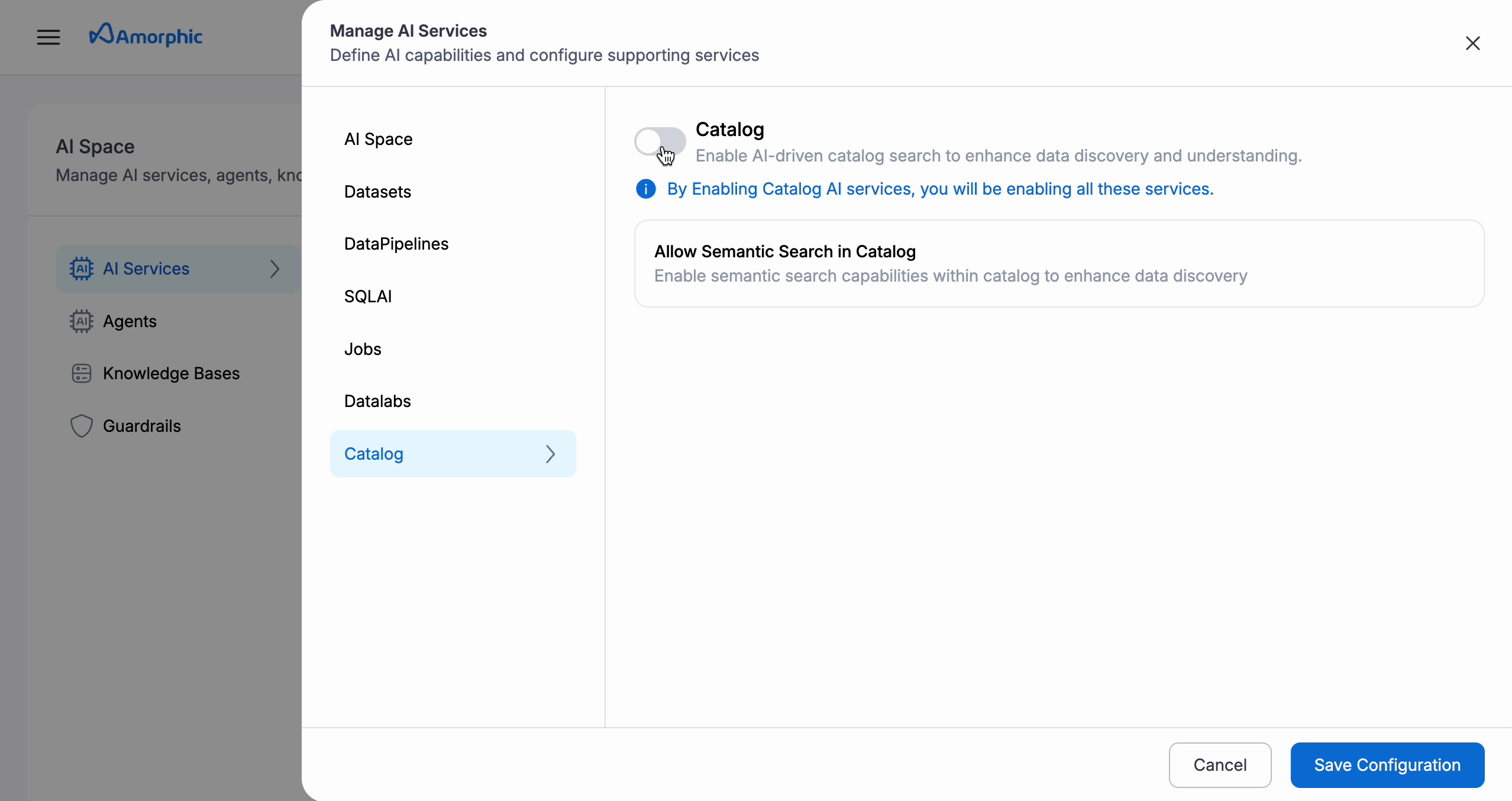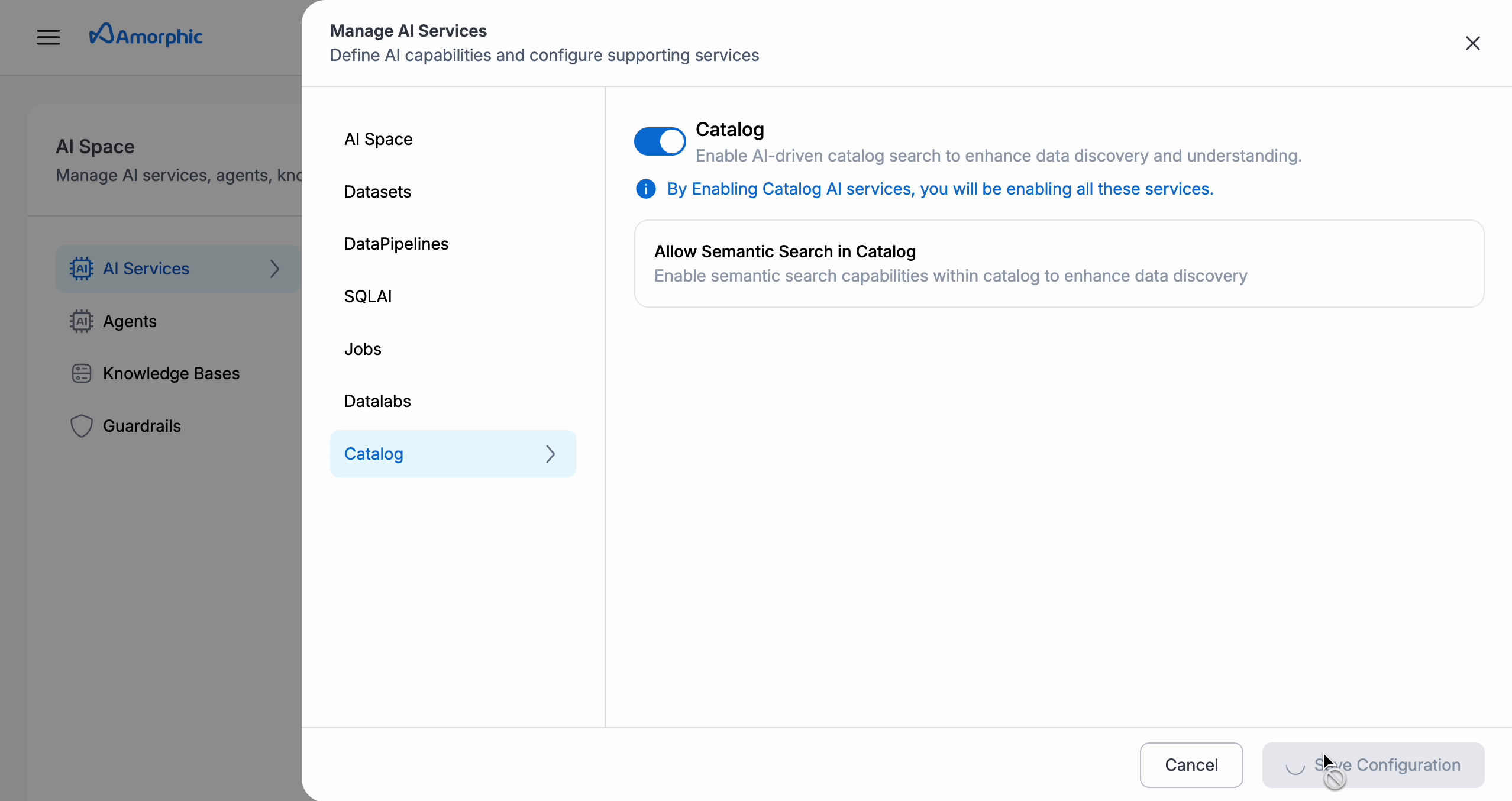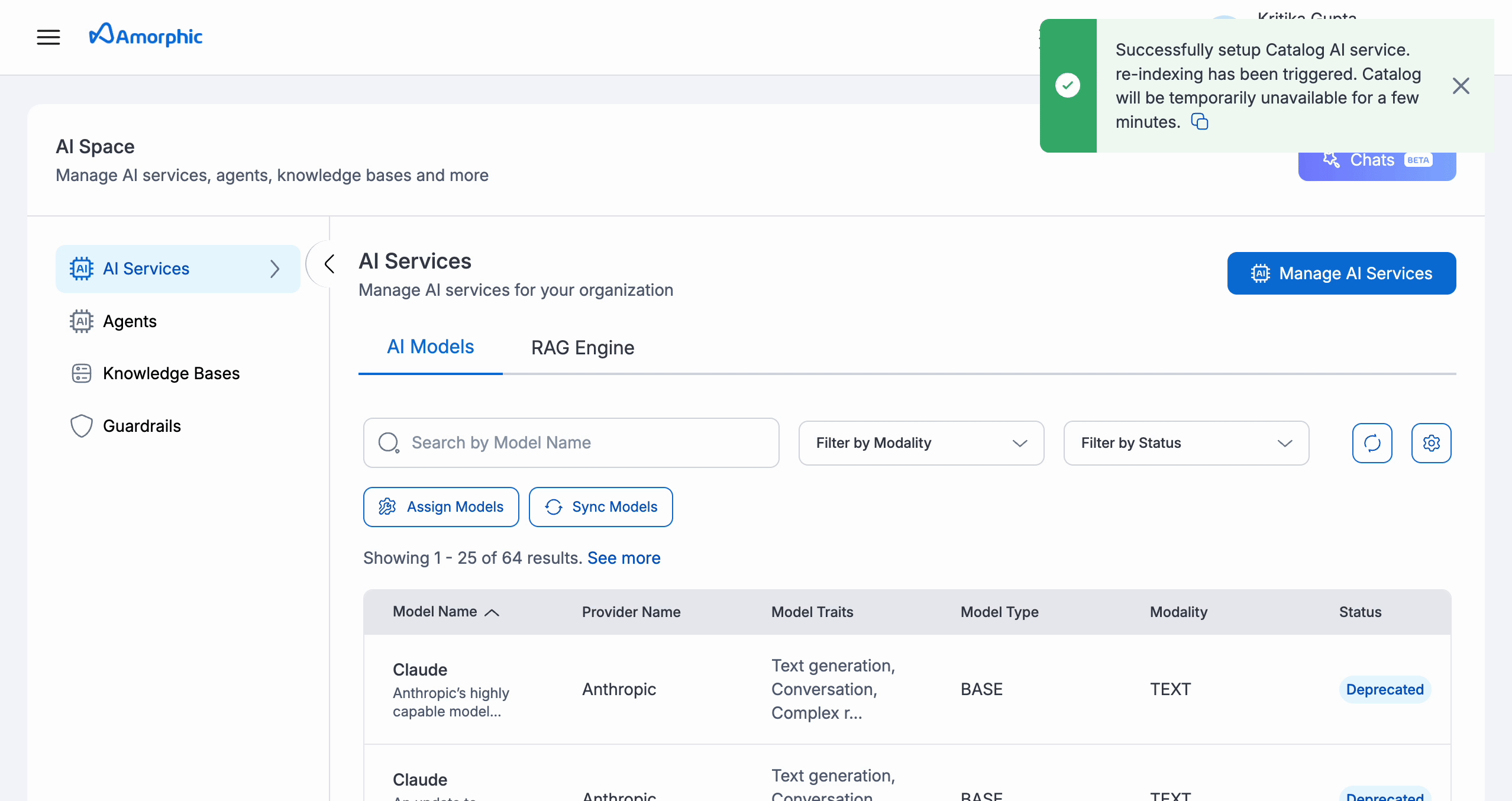
Default Search Type:
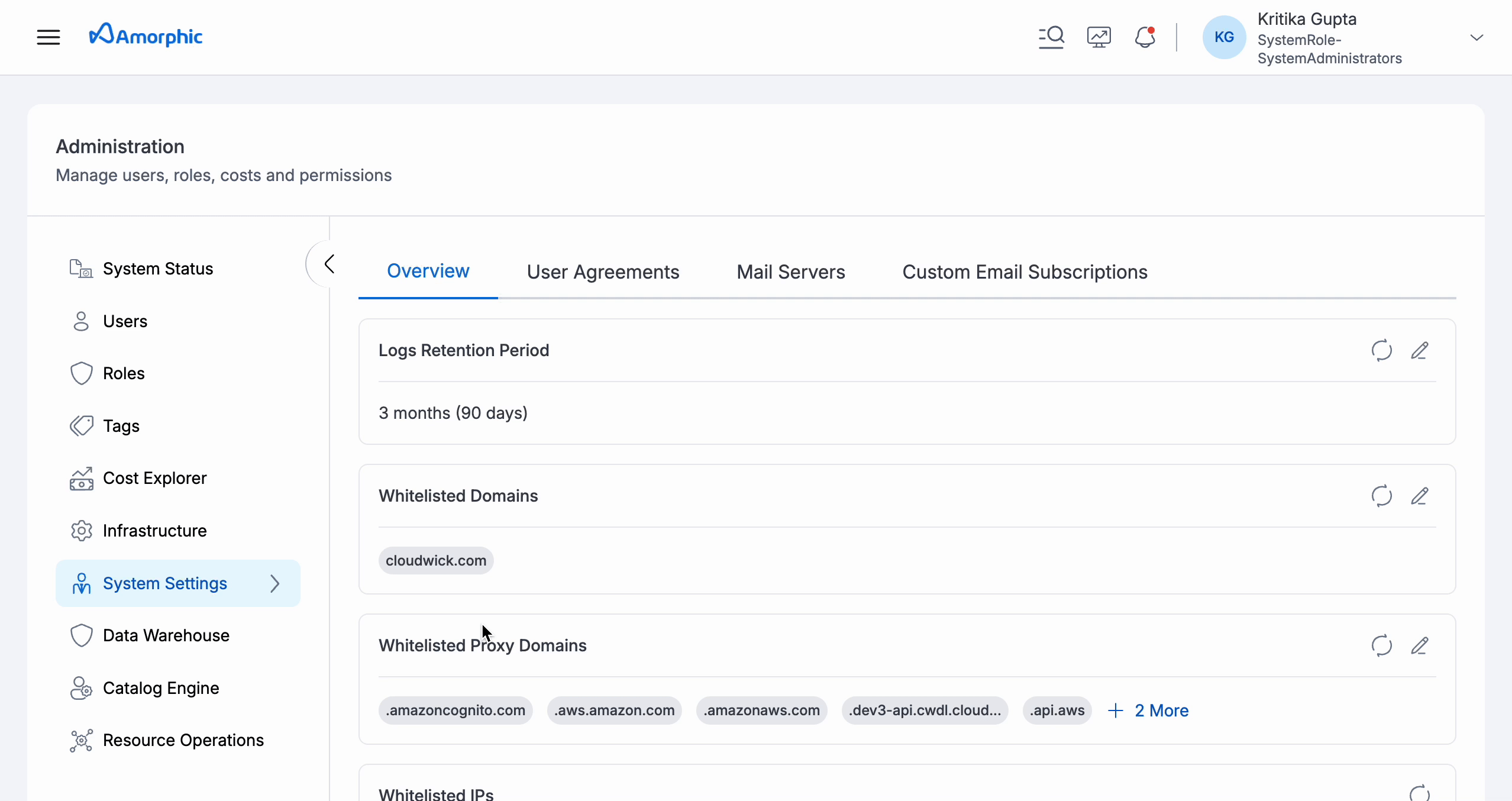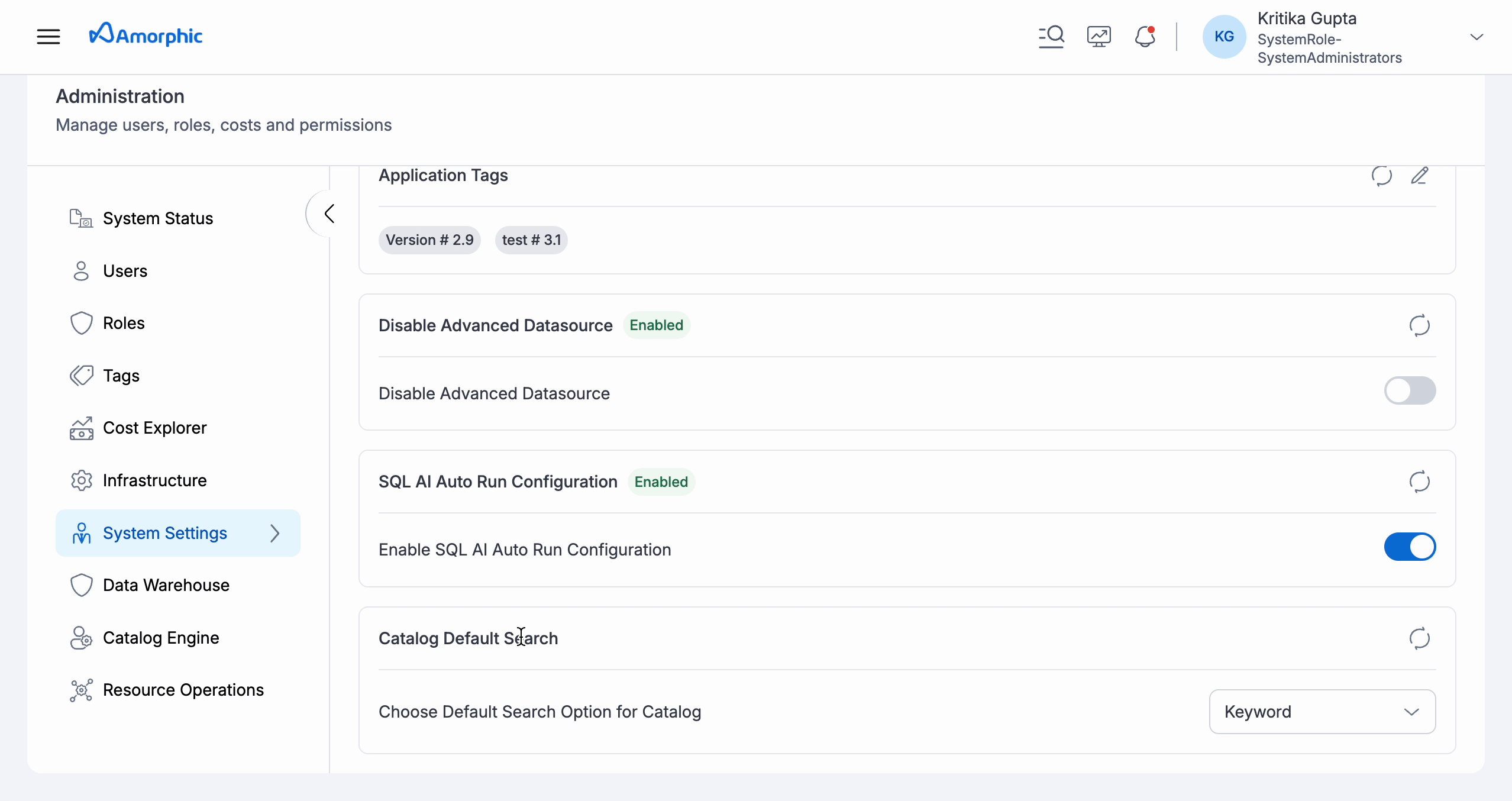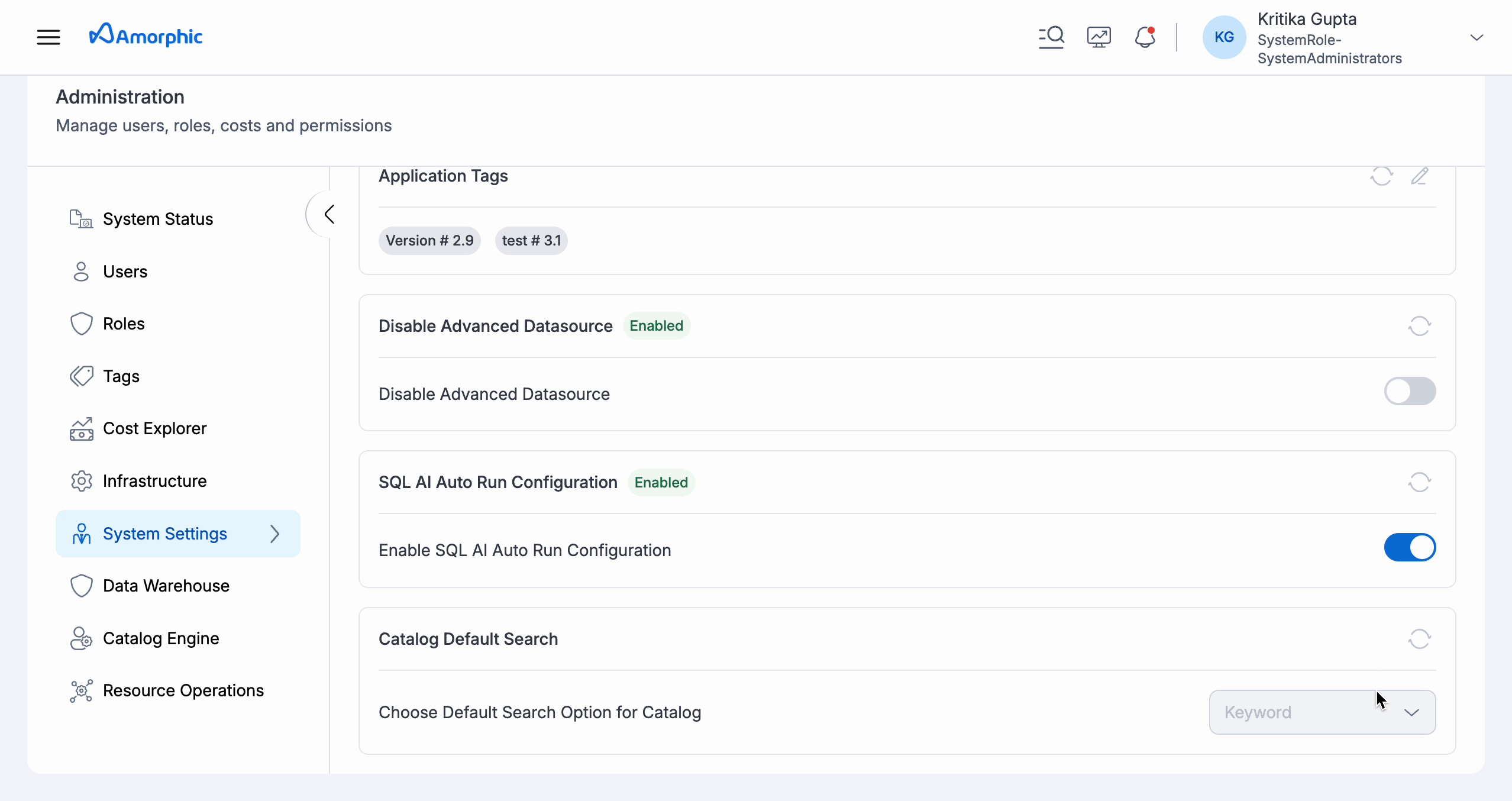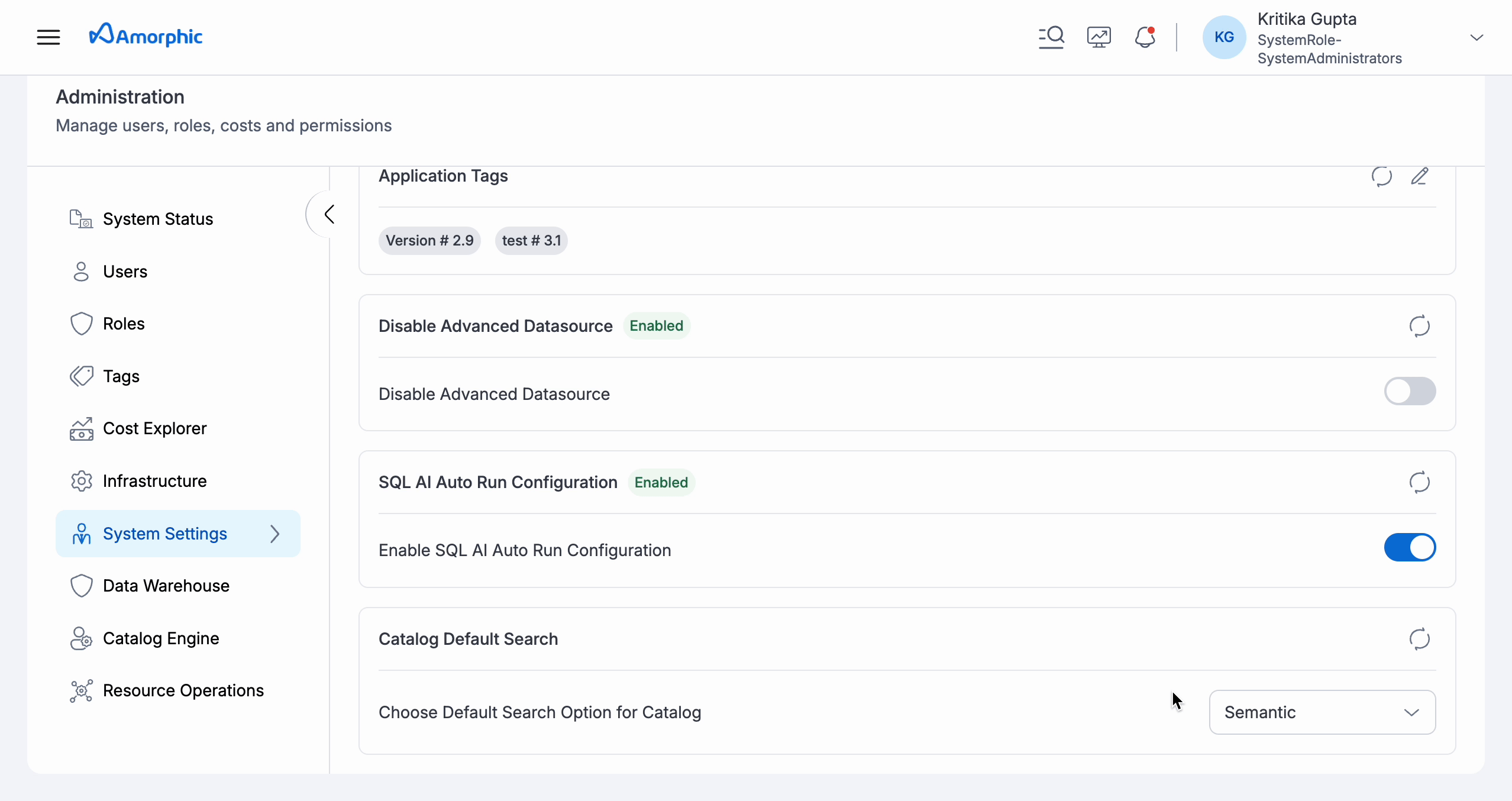
You can set the default search type to be used for your Catalog search queries within the System Settings tab of Administration section within Amorphic. This selection can be changed anytime and can be overridden by the search type selection made while hitting the search query in Catalog.
Initial Setup
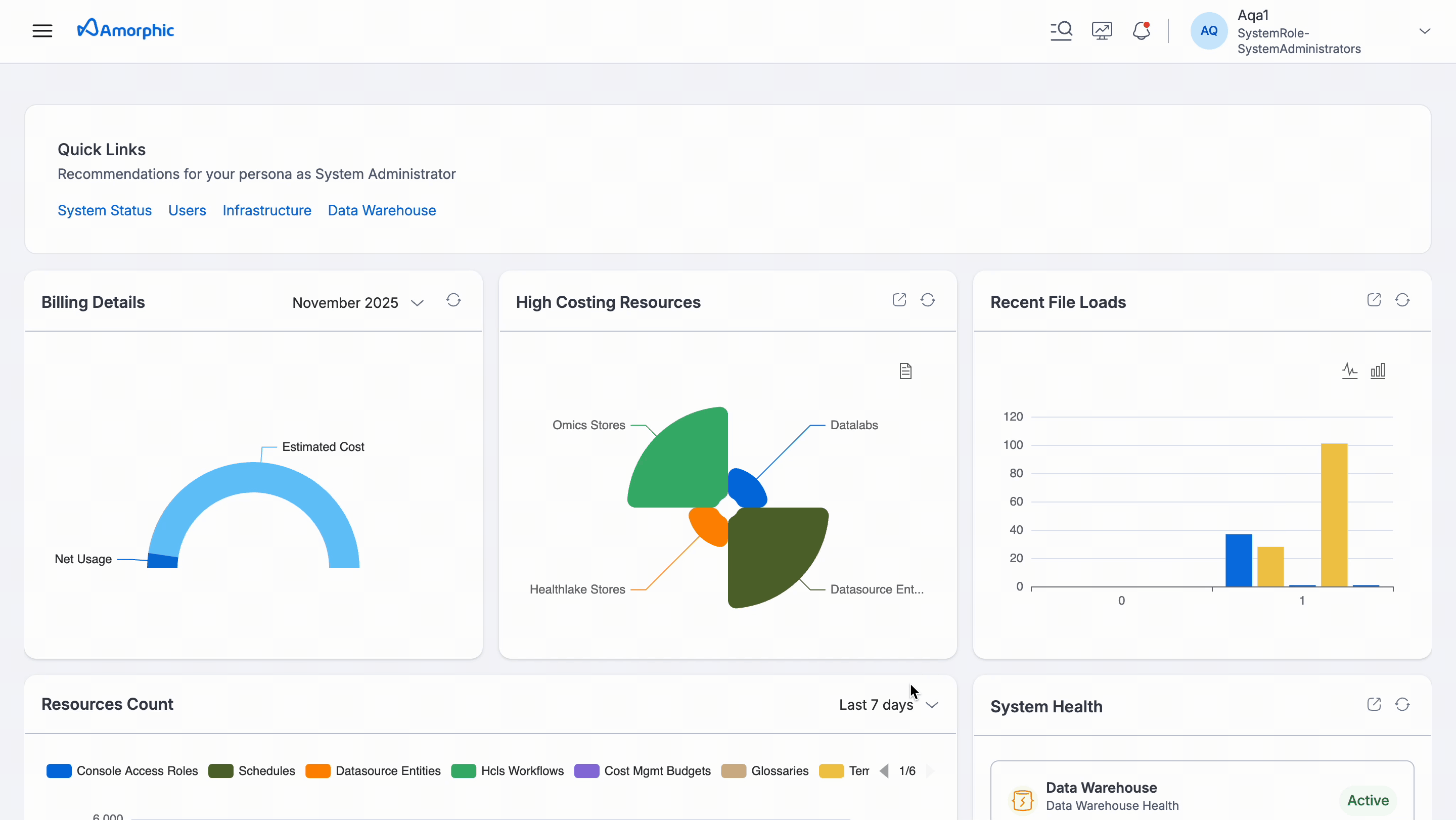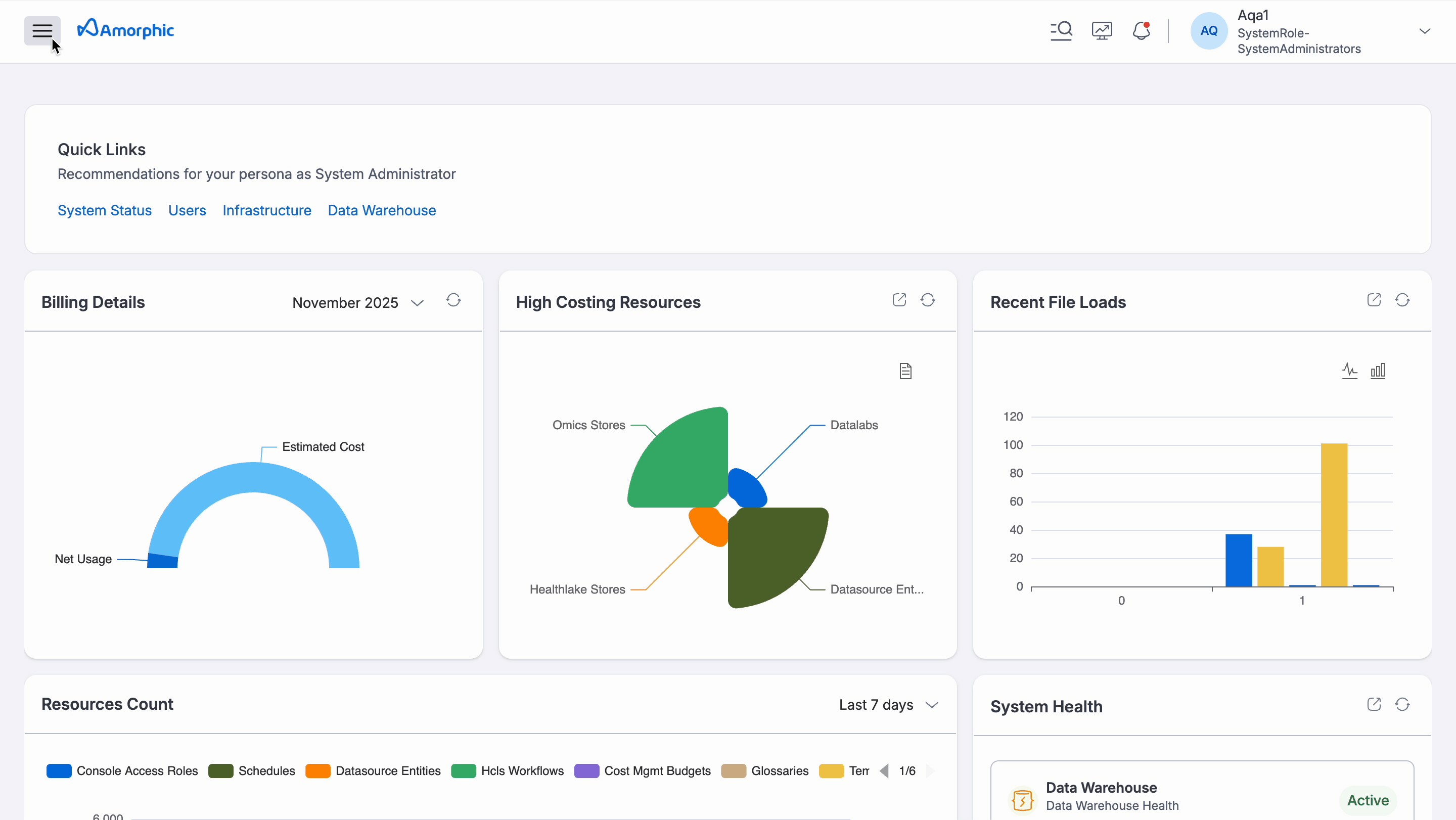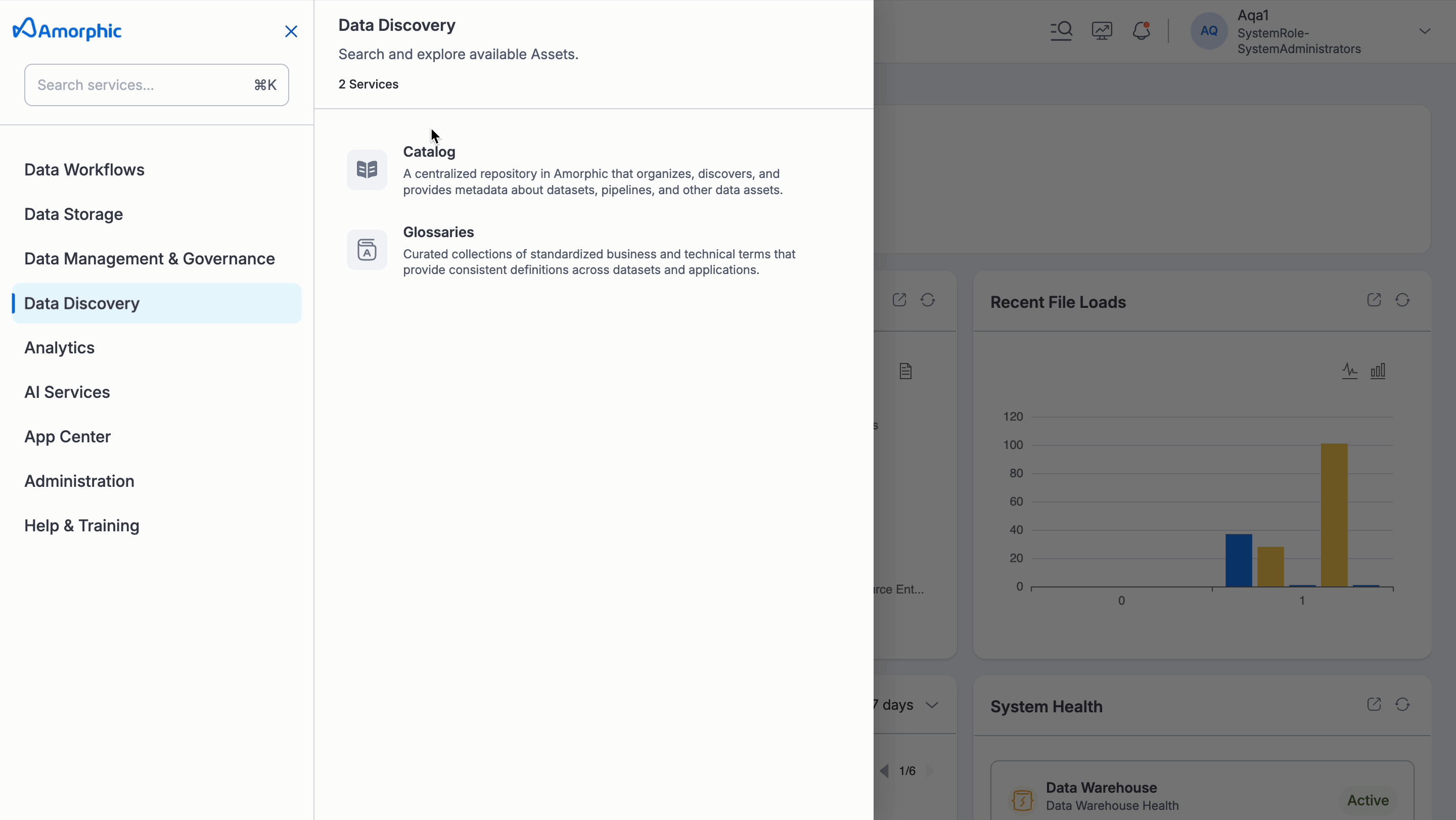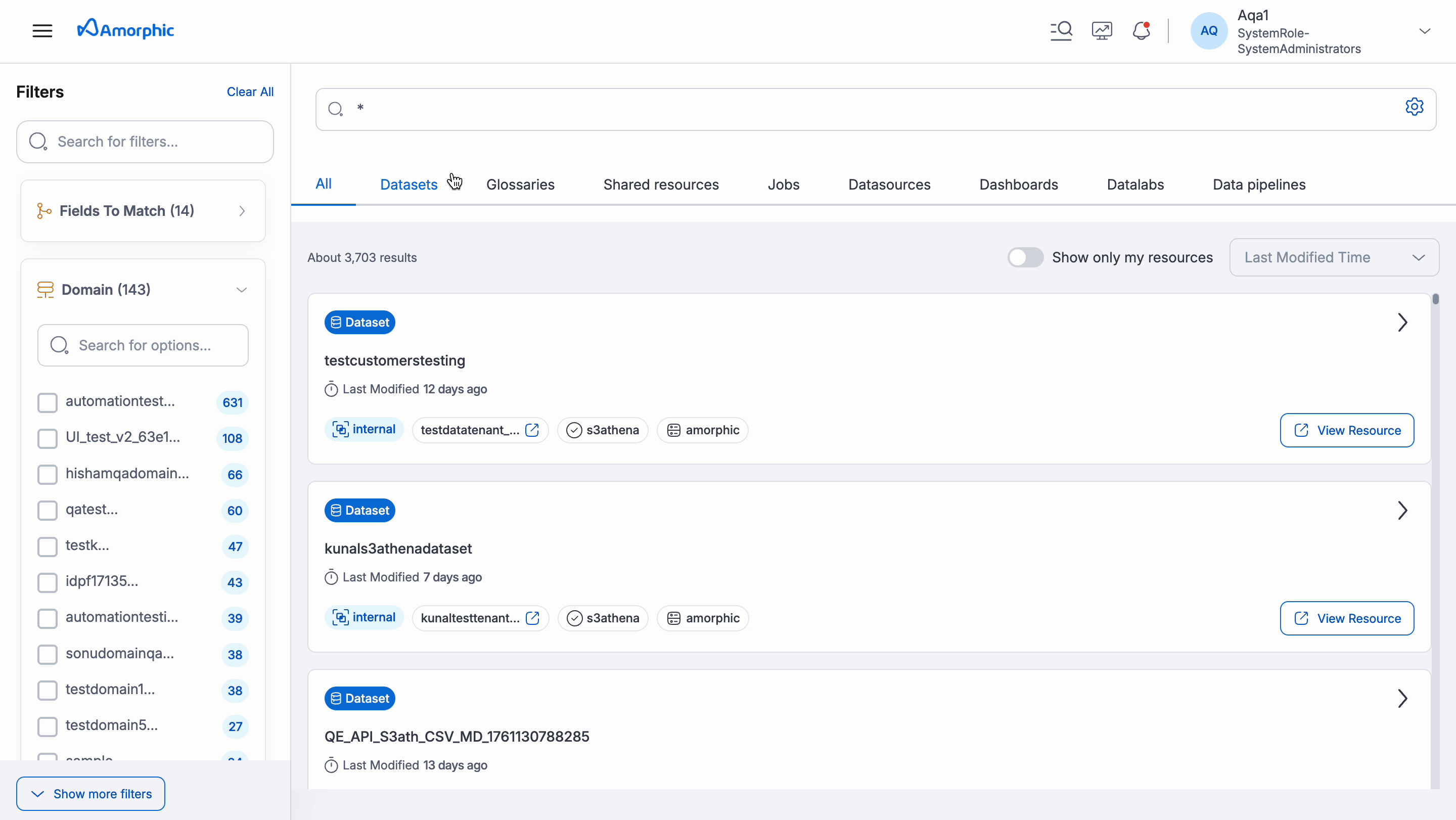
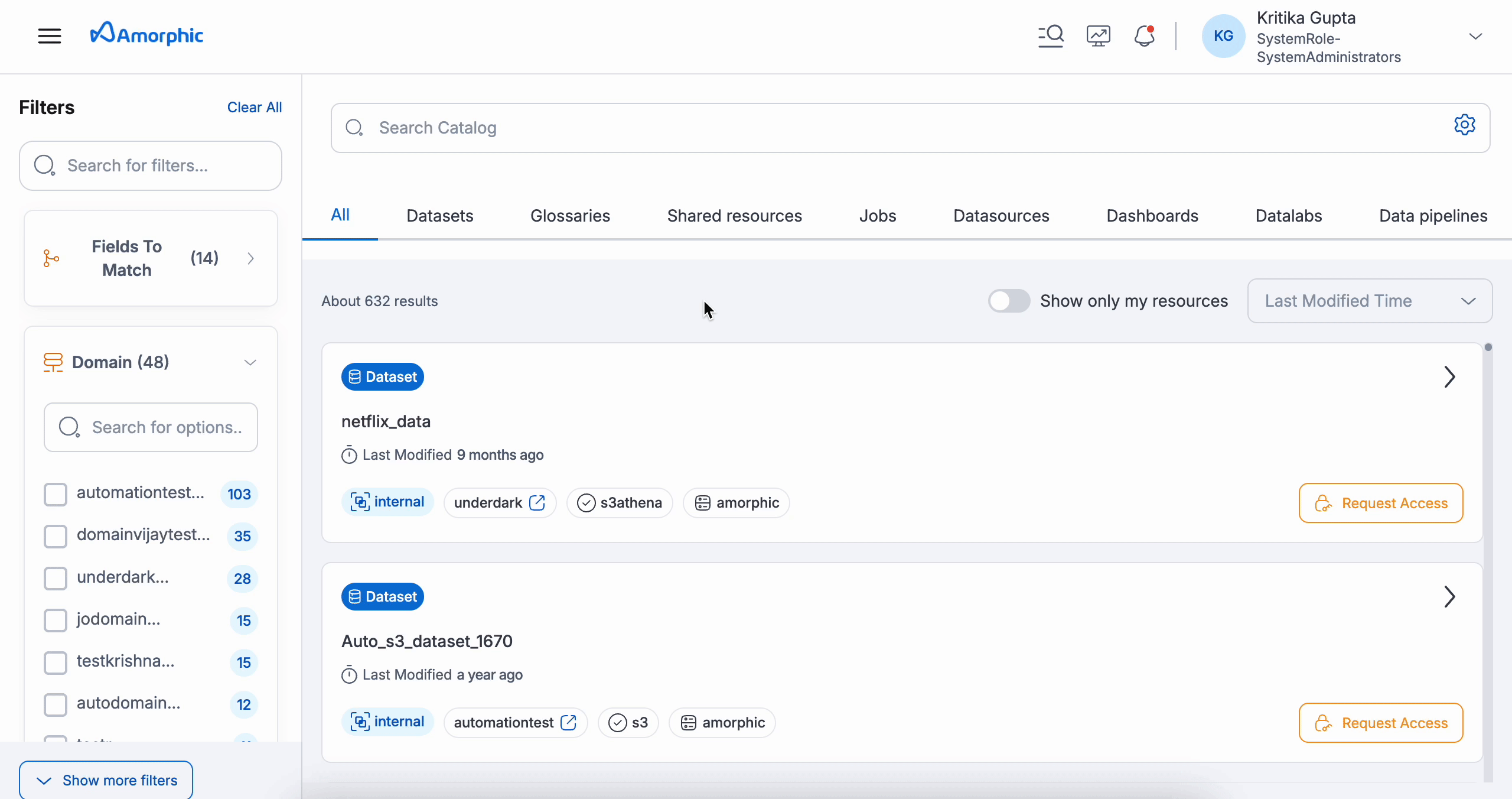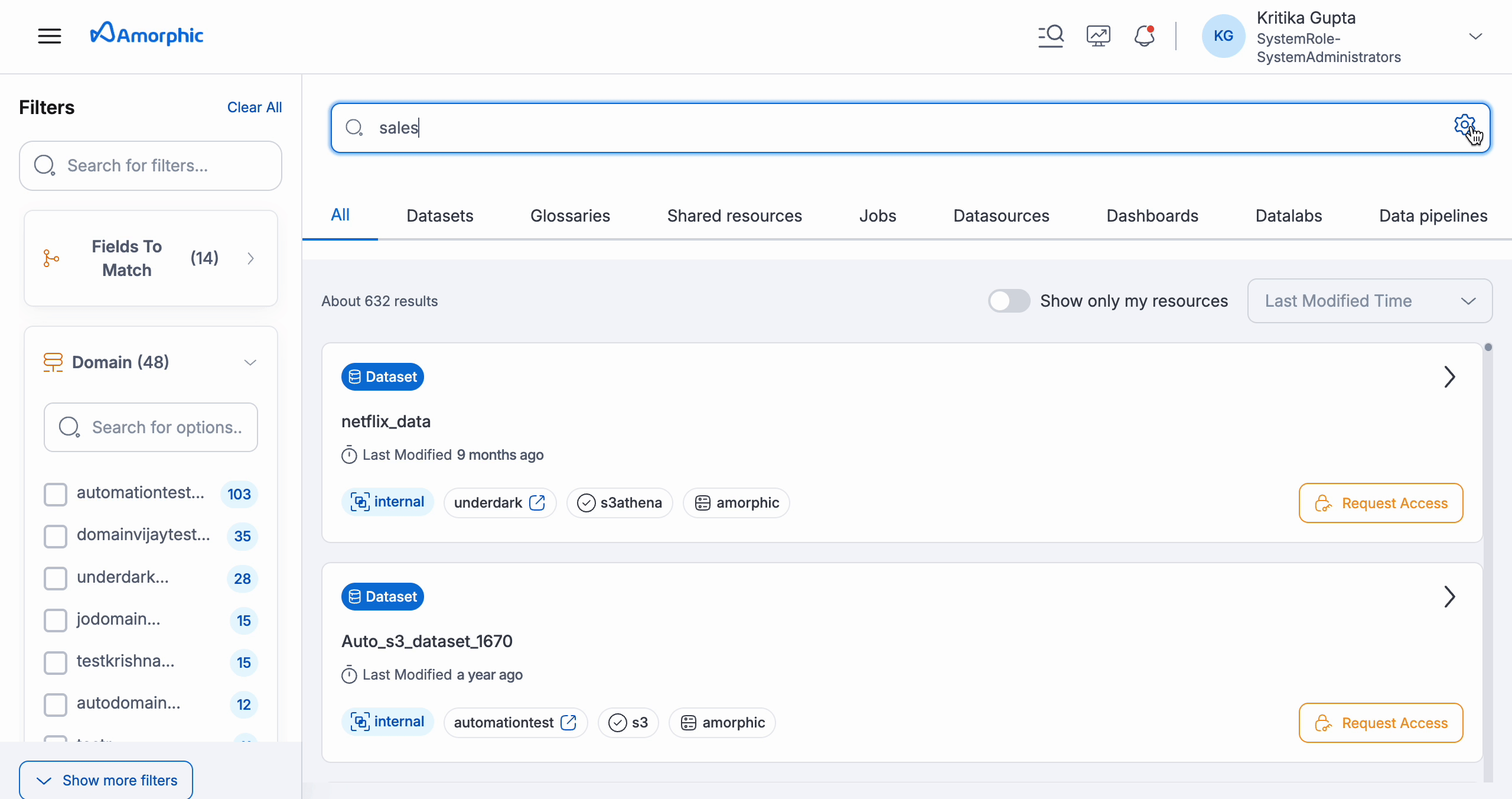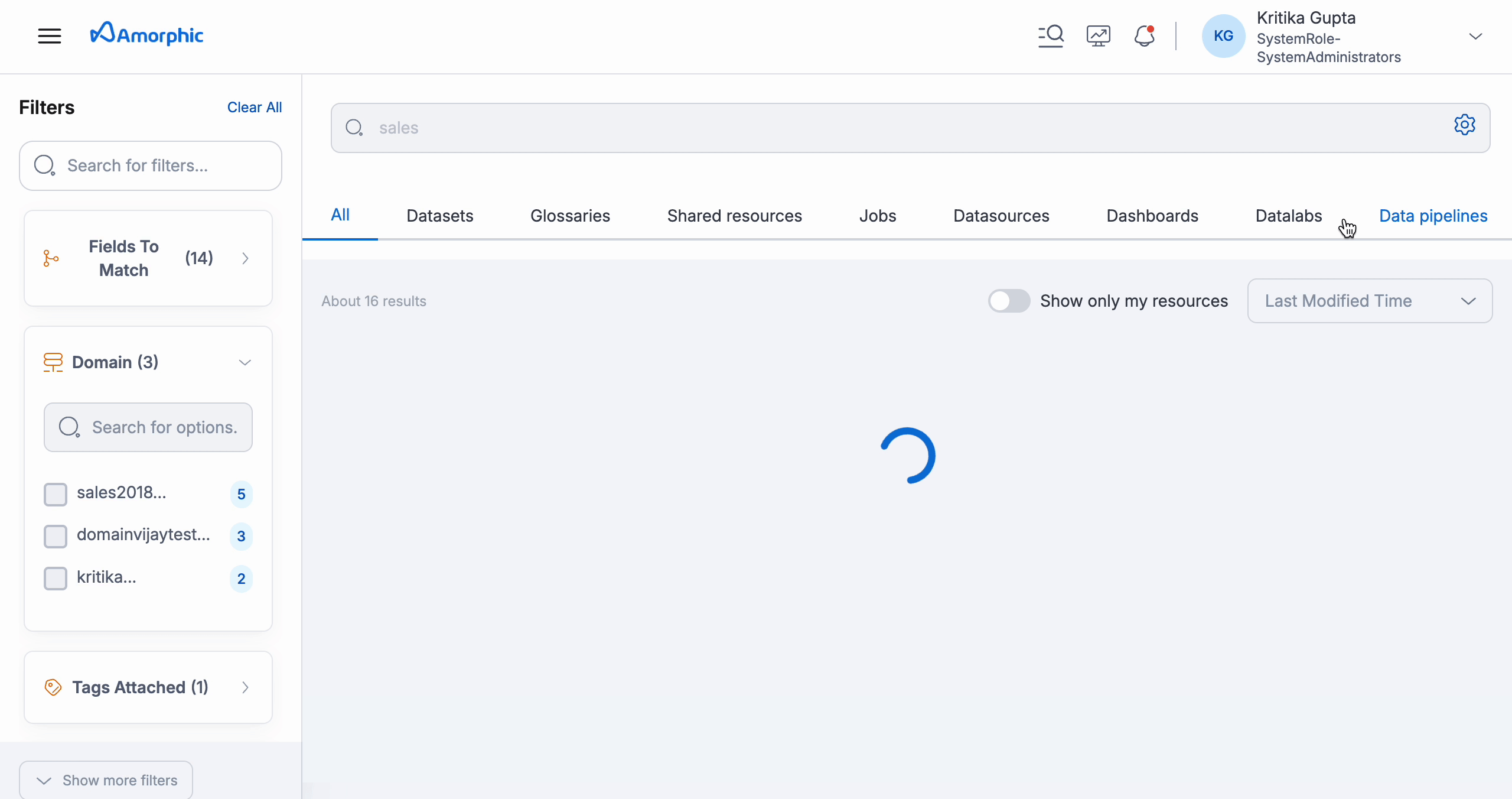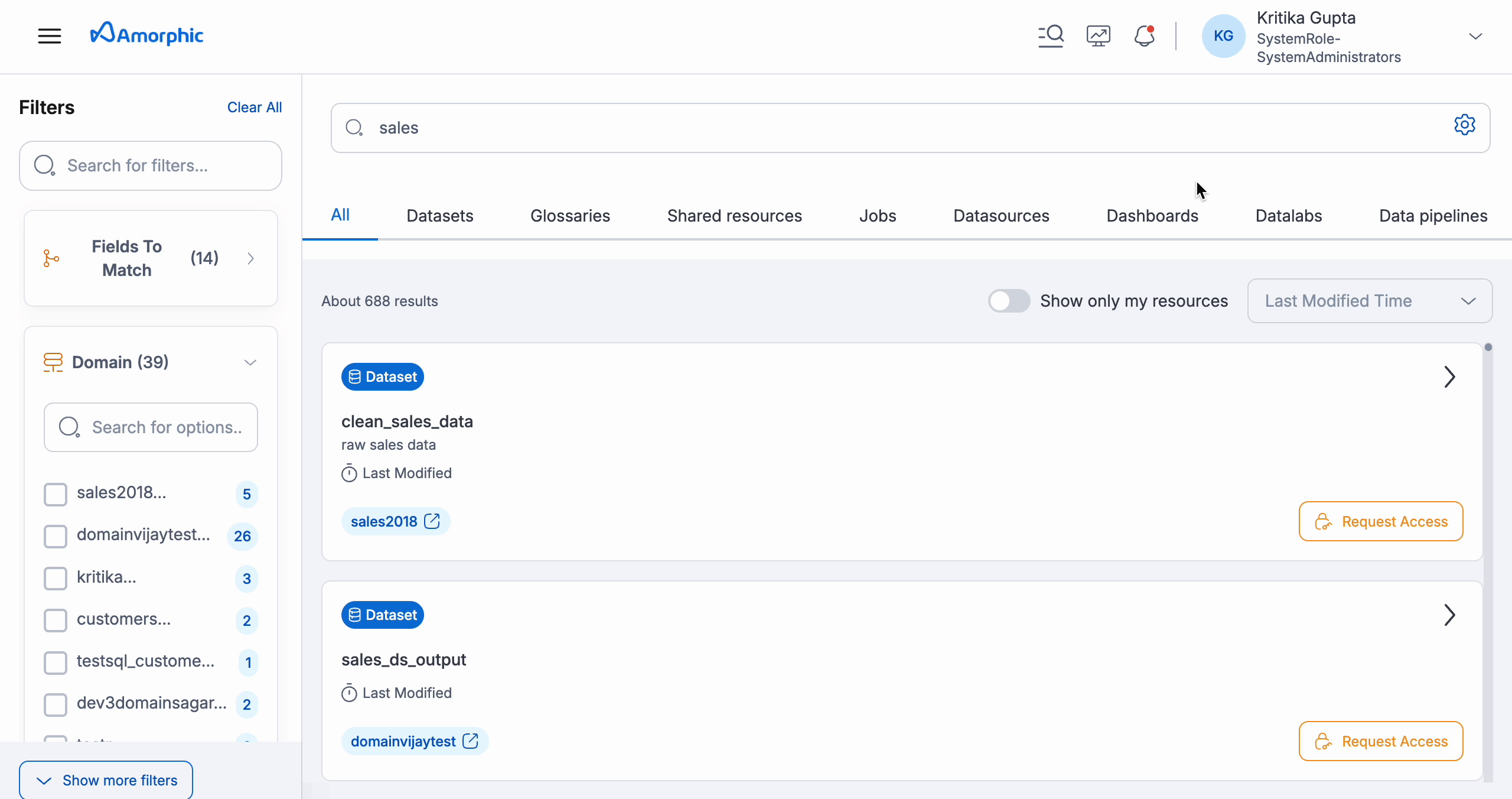
- Search Bar: Located on the homepage, it allows users to type in their search terms. The system displays the total number of available resources.
- Select Search Type: Use the gear icon in the search bar to choose your preferred search type (Keyword or Semantic) for the query. The search type you selected for your last query will be marked with a check mark. The default search type configured by your administrator in System Settings will also be highlighted.
- Catalog Datasource Sync Job: If the Catalog page shows no resources, run the "Catalog Datasource sync job". This synchronizes resource metadata with the catalog and only needs to be done once to get everything indexed. This process is intended to index all existing assets.
Optimizing and Refining Search with Filters
Understanding Filters
The Filters section is located to the left of the search bar, where users can find filters to narrow down their search.
Available Filters:
- Domain
- Data Classification
- Tags Attached
- Keywords
- Target Location
- File Type
- Asset Type
- Tenant
- Datasource Type
By default the following filter options will be shown in the Catalog page:
- Fields to Match
- Domain
- Data Classification
- Tags
You can click on the Show more filters button to be able to see the other filters as well. The additional filters can be collapsed back by using the Hide filters button.
Managing Search Results
Time and Access Based Filters
Users can filter search results by Last Modified Time (All Time, Last 24 Hours, Last 7 Days, Last 30 Days, Last 90 Days, Last Year) and toggle My Resources to show only their own assets.
Filter by Fields on Search Results
Users can apply filters on fields to the search results. The Fields to Match section is located at the top of the filters section. Users can pick specific fields from the 'Fields to Match' section to match the search query for more accurate results.
Specifying Fields
The "Any" Field Option
There's an "Any" field option that searches across all available fields. However, this can slow down the query and may cause timeouts. For better results, specify the field name.
Advanced Search Techniques
Fuzzy Query
Use the tilde symbol (~) to find similar terms. For example, "Appel~" will find results for "Apple". Increase the number of characters using "~4" to extend the search (e.g., Appel~4).
- Replacements: "cat" to "bat"
- Insertions: "cat" to "cats"
- Deletions: "cat" to "at"
- Transpositions: "cat" to "act"
Regex Query
Enclose the query in forward slashes (/) to find documents matching a specific pattern. For example: /App.*/ to find terms starting with "App". Note that special characters might cause errors.
Important Considerations
Access Control
If a tenant is selected that the user does not have access to, the result will show "No Assets Found".
Supported Assets
As of version 3.1, the catalog search supports Datasets, Datasources, Datalabs, Data Pipelines, Jobs, Dashboards, Glossaries and Shared resources such as Libraries, Datalab Lifecycle Configurations and Code Repositories.