Assets
What is a Data Asset?
Think of a data asset as a valuable piece of data that's been registered in Amorphic. This could be a dataset like structured or unstructured data holding or a glossary. Each data asset comes with metadata, which is like a detailed description covering what the data is about, where it came from, how it's structured, and how it can be used. This makes it easier for user to find the data needed, understand it, and use it effectively for analysis, reporting, and making informed decisions.
Finding Data Assets
This section helps users find, understand, and use data assets within Amorphic. Users can easily find and explore assets using the Amorphic Catalog feature.
Key Features
-
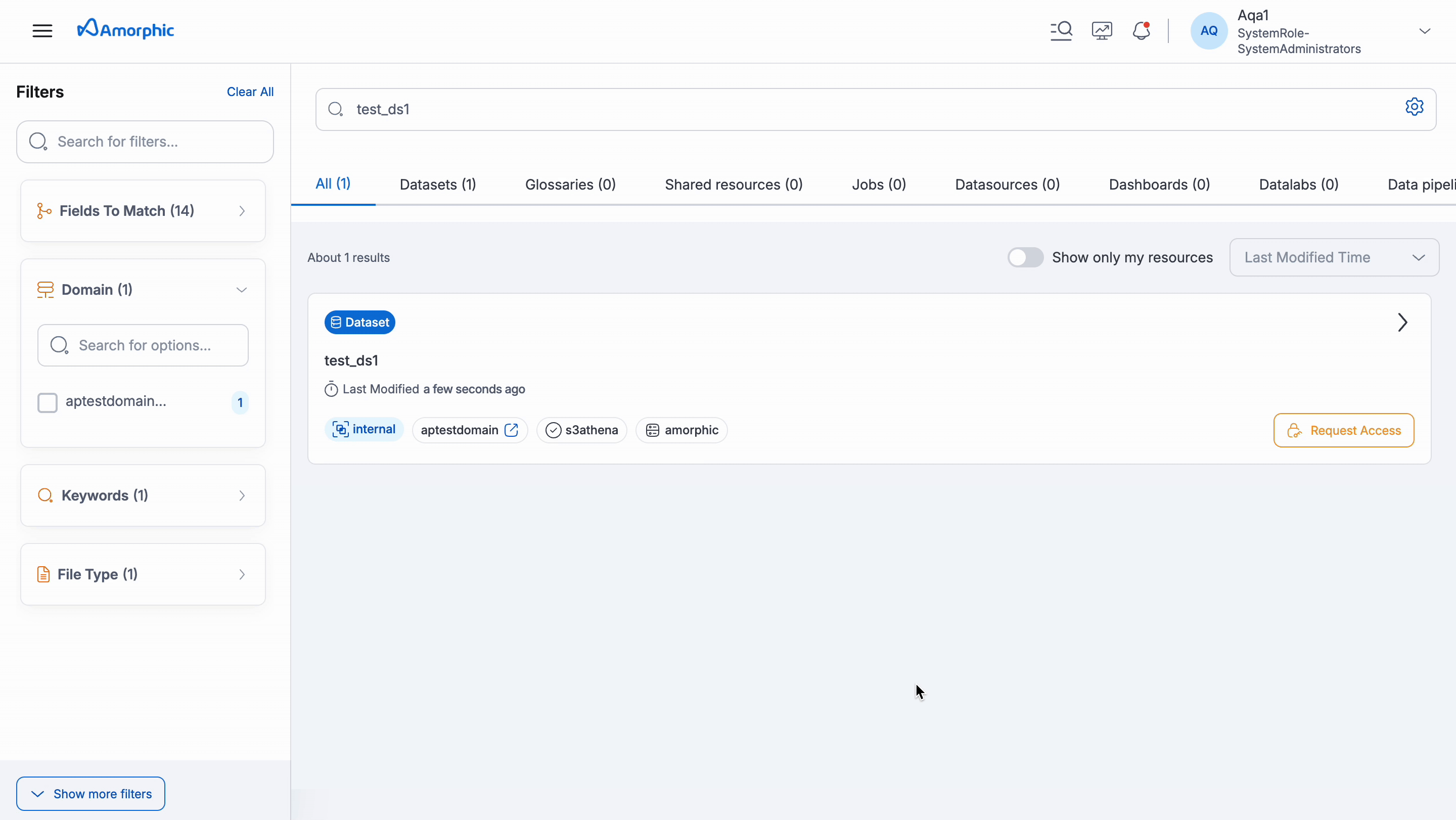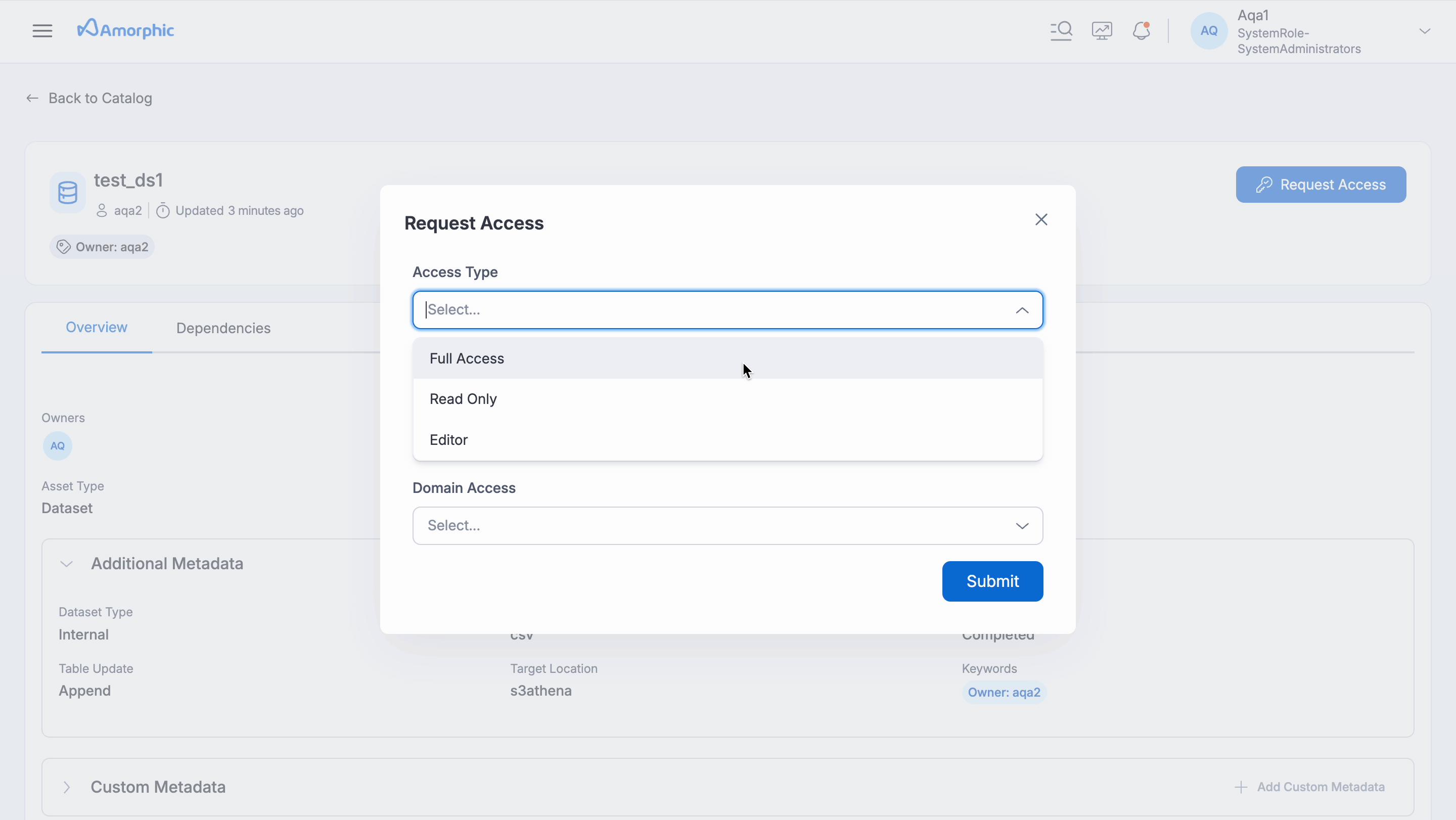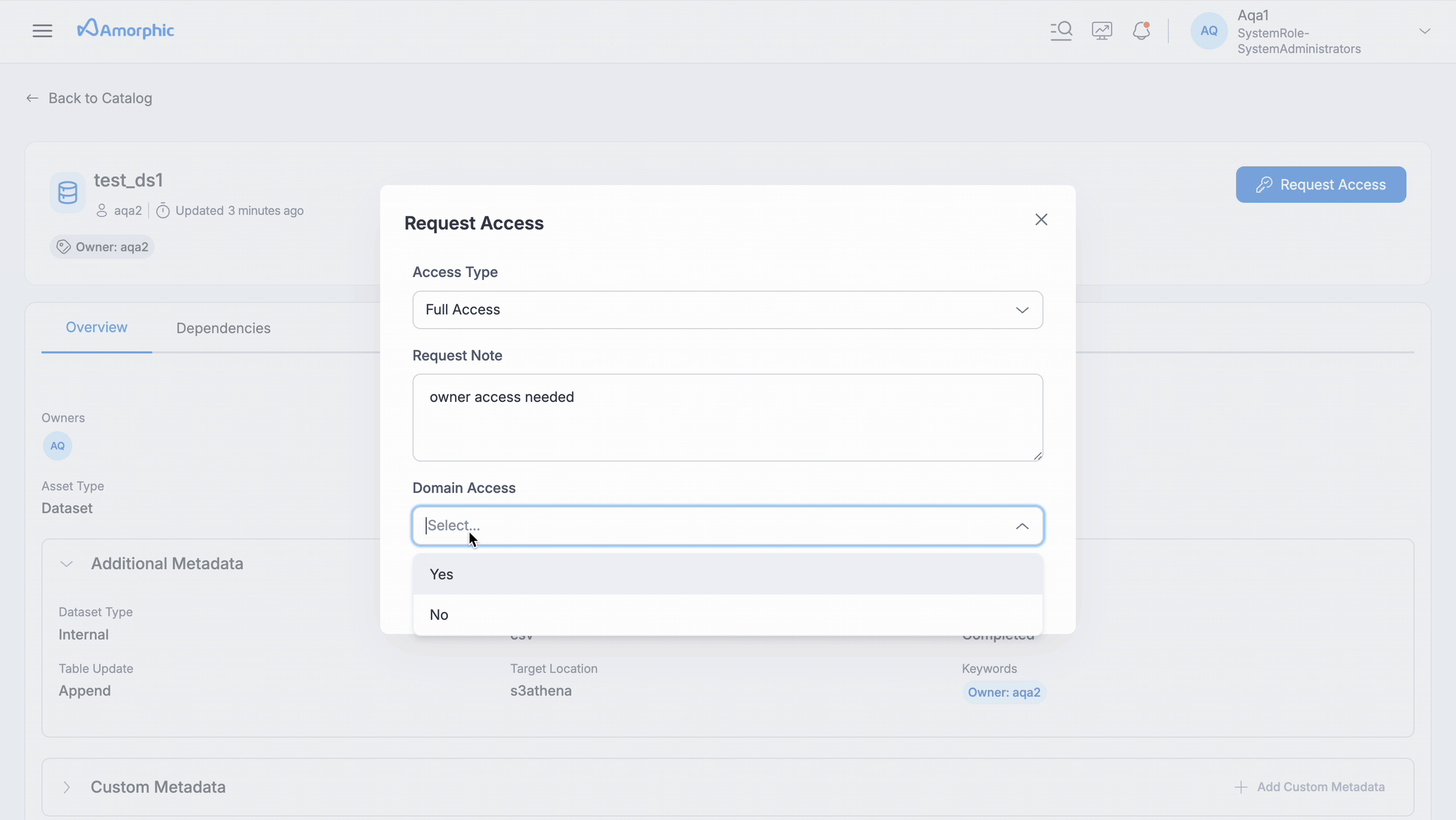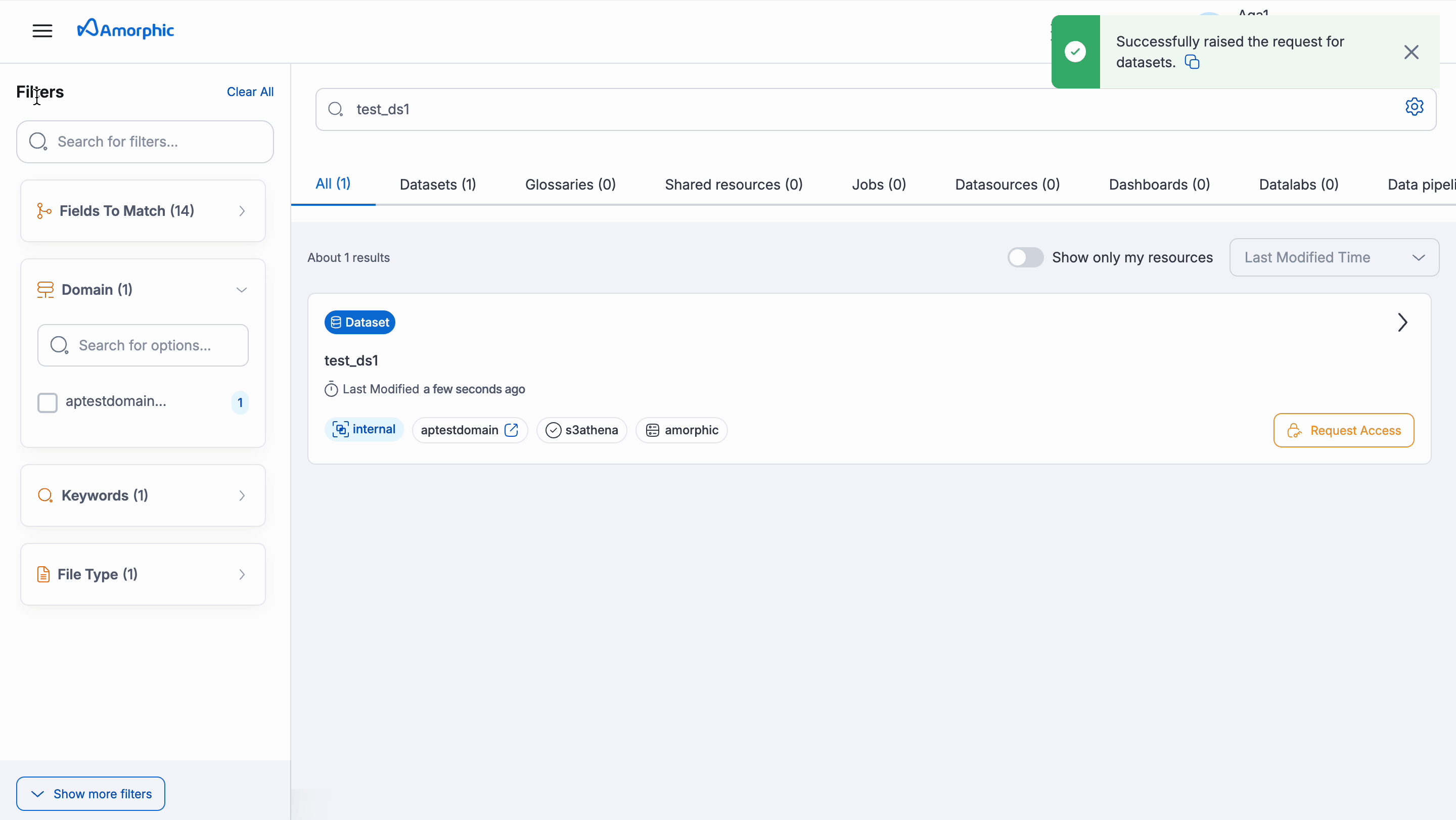
Requesting Access: If user finds an asset that they need but don't have access, user can request permission directly within Amorphic.
 If user has access to the undelying resource, they will be able to navigate to it.
If user has access to the undelying resource, they will be able to navigate to it.
-
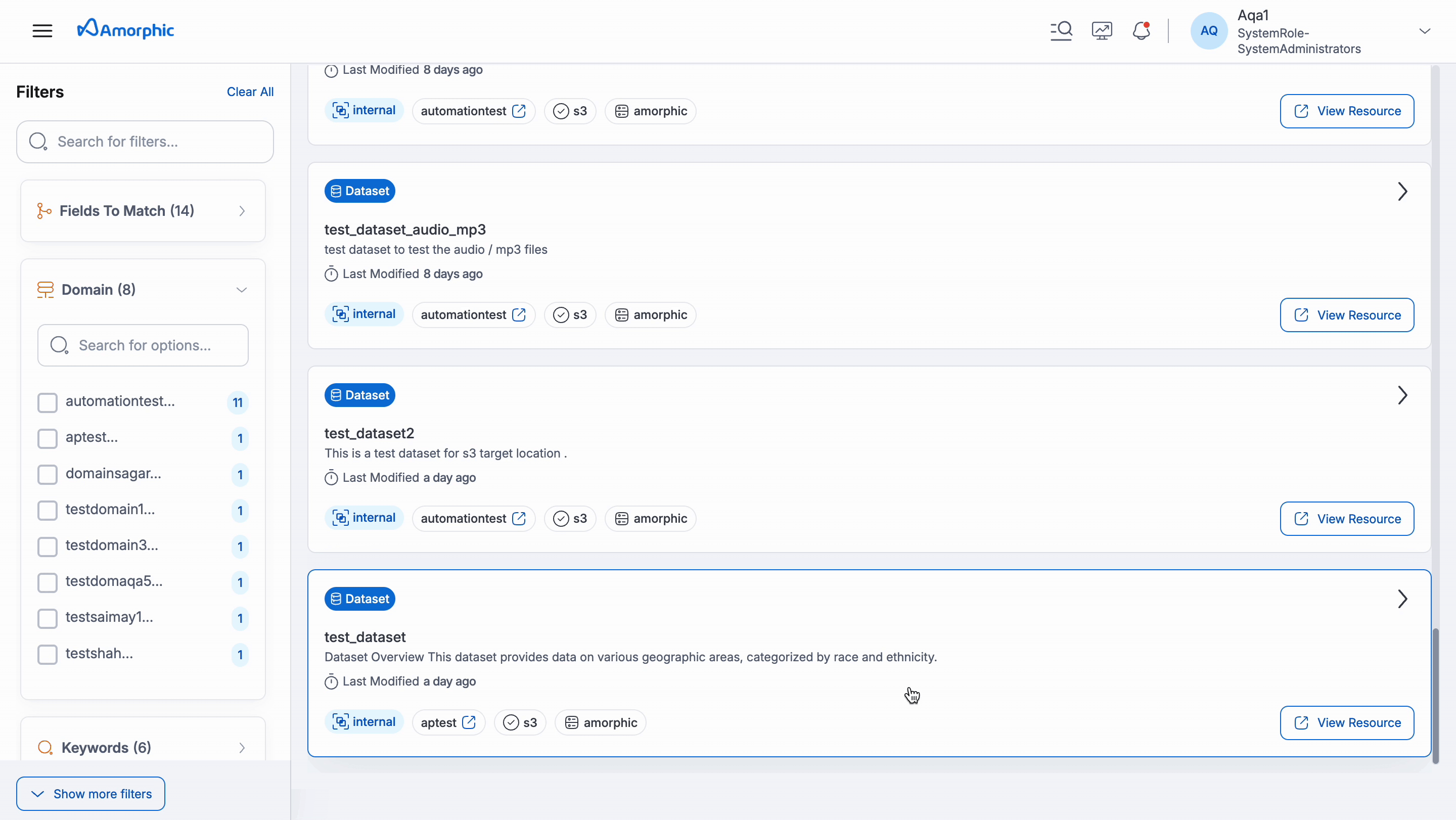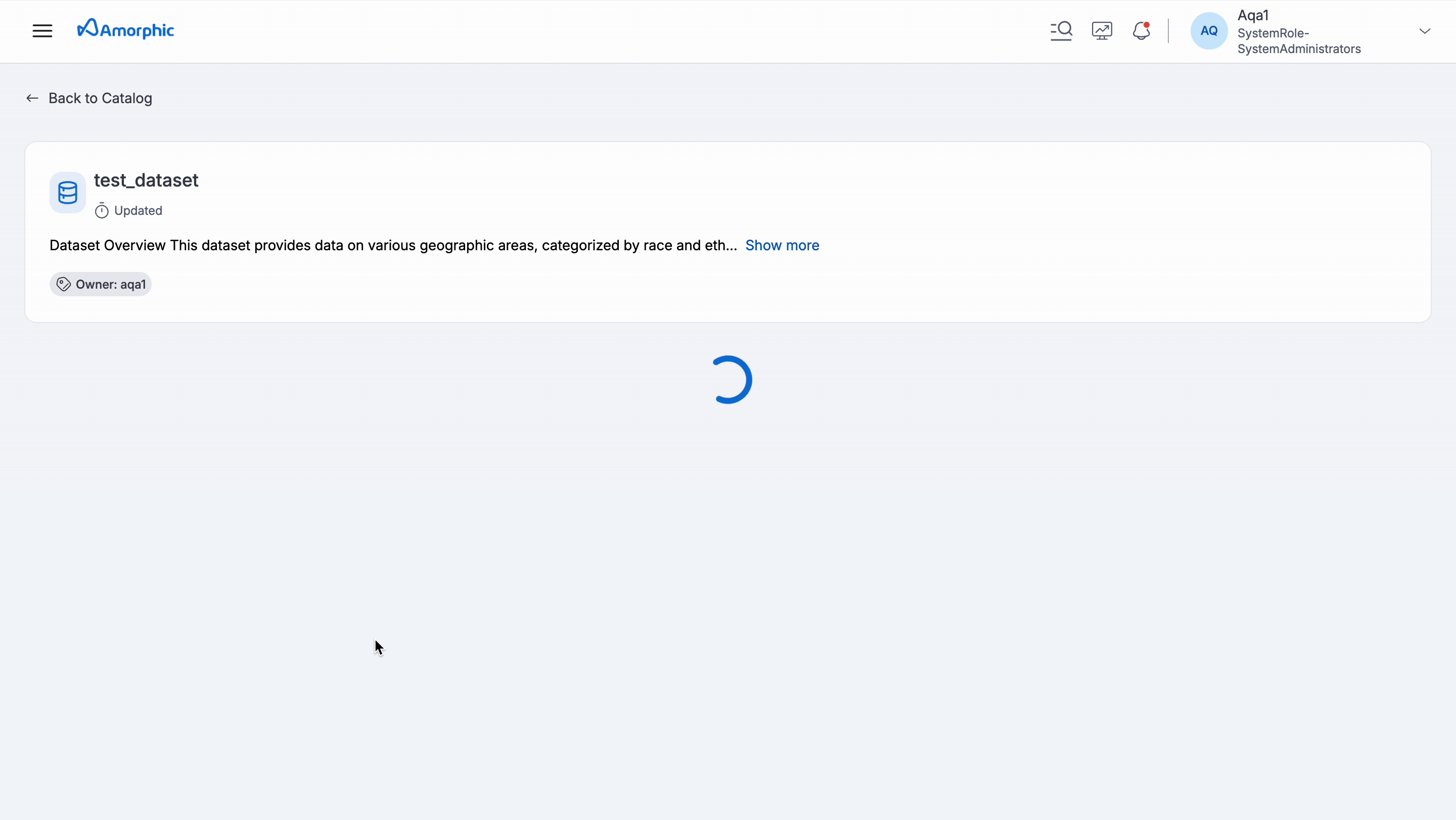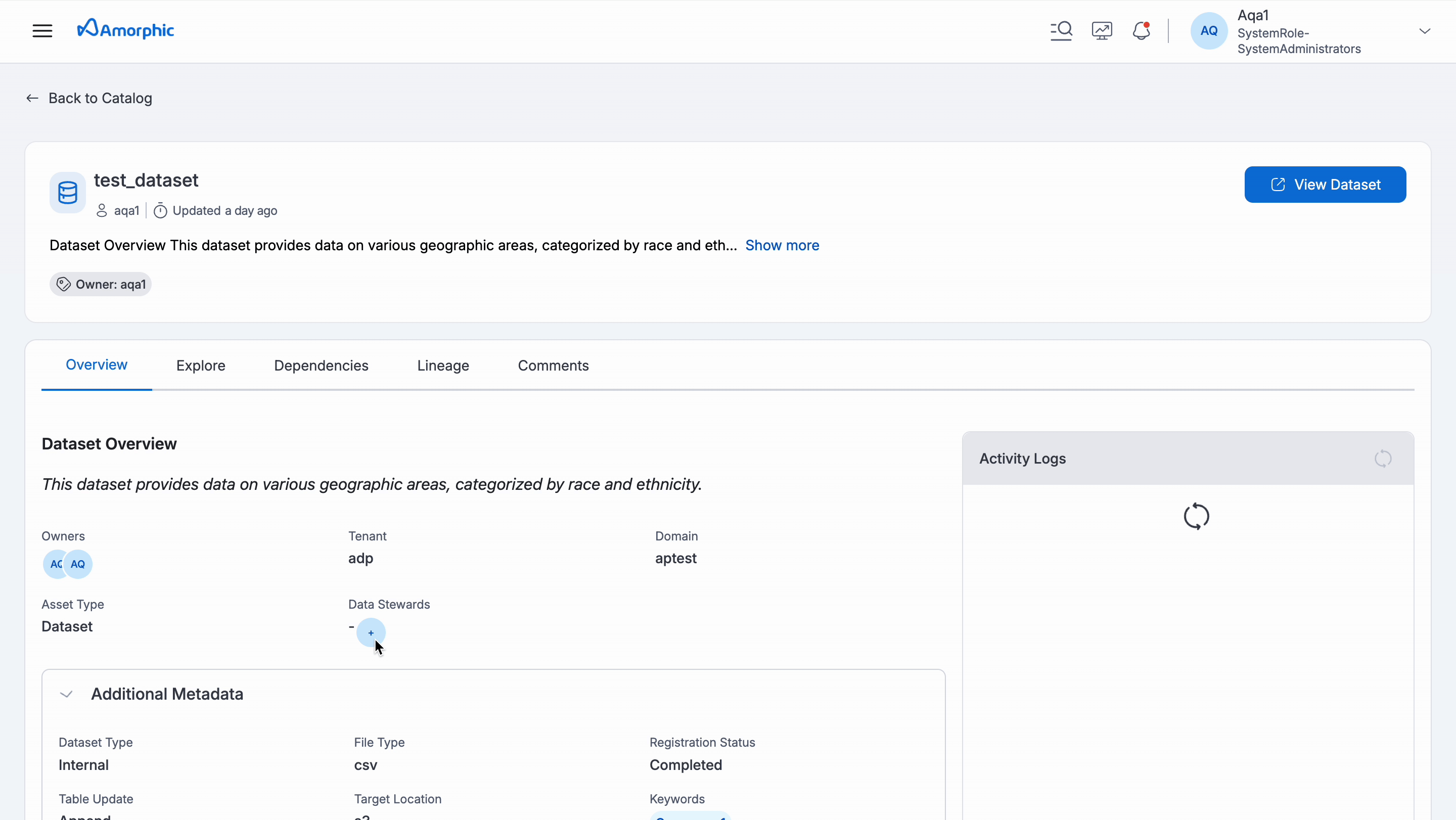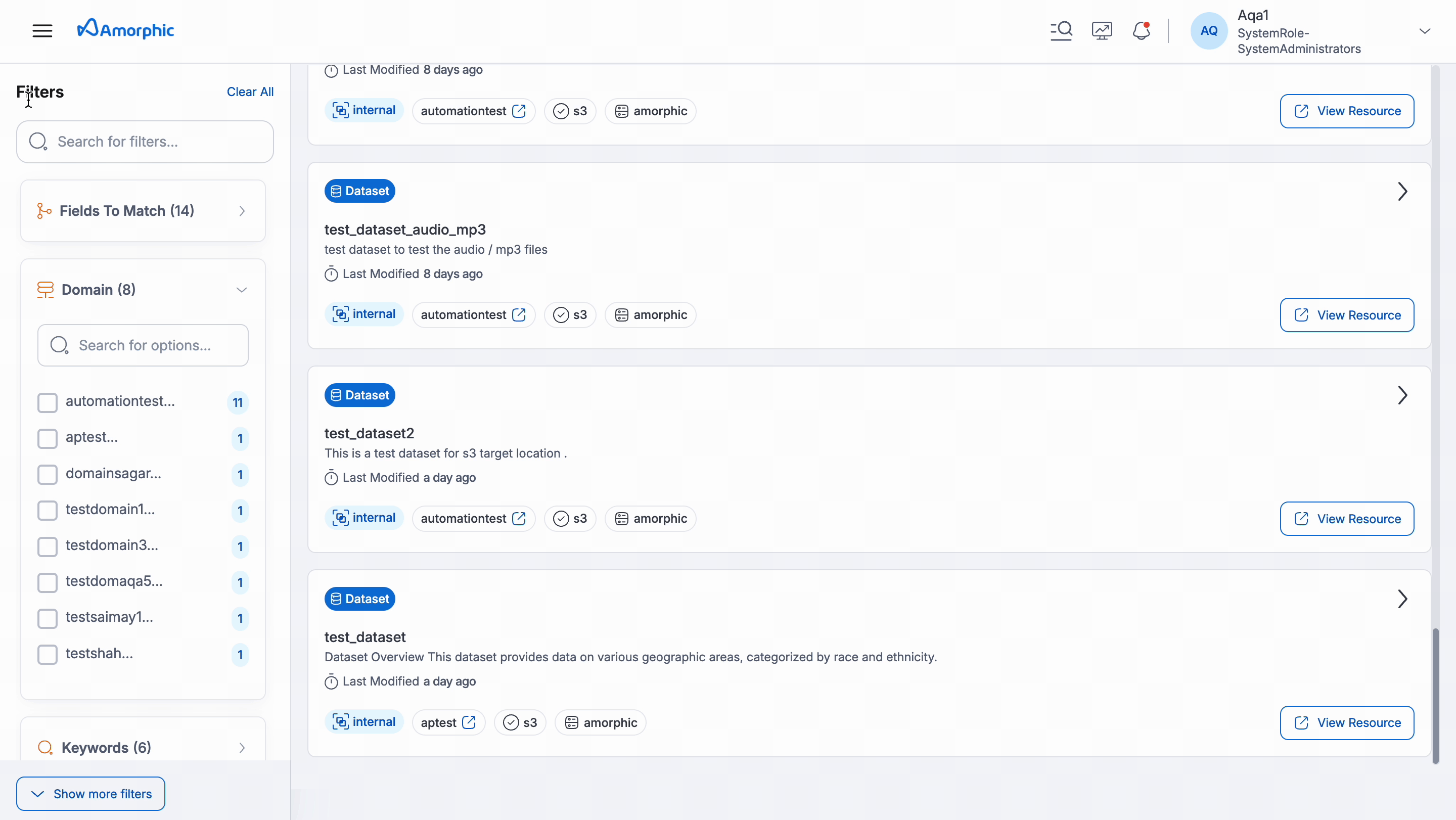
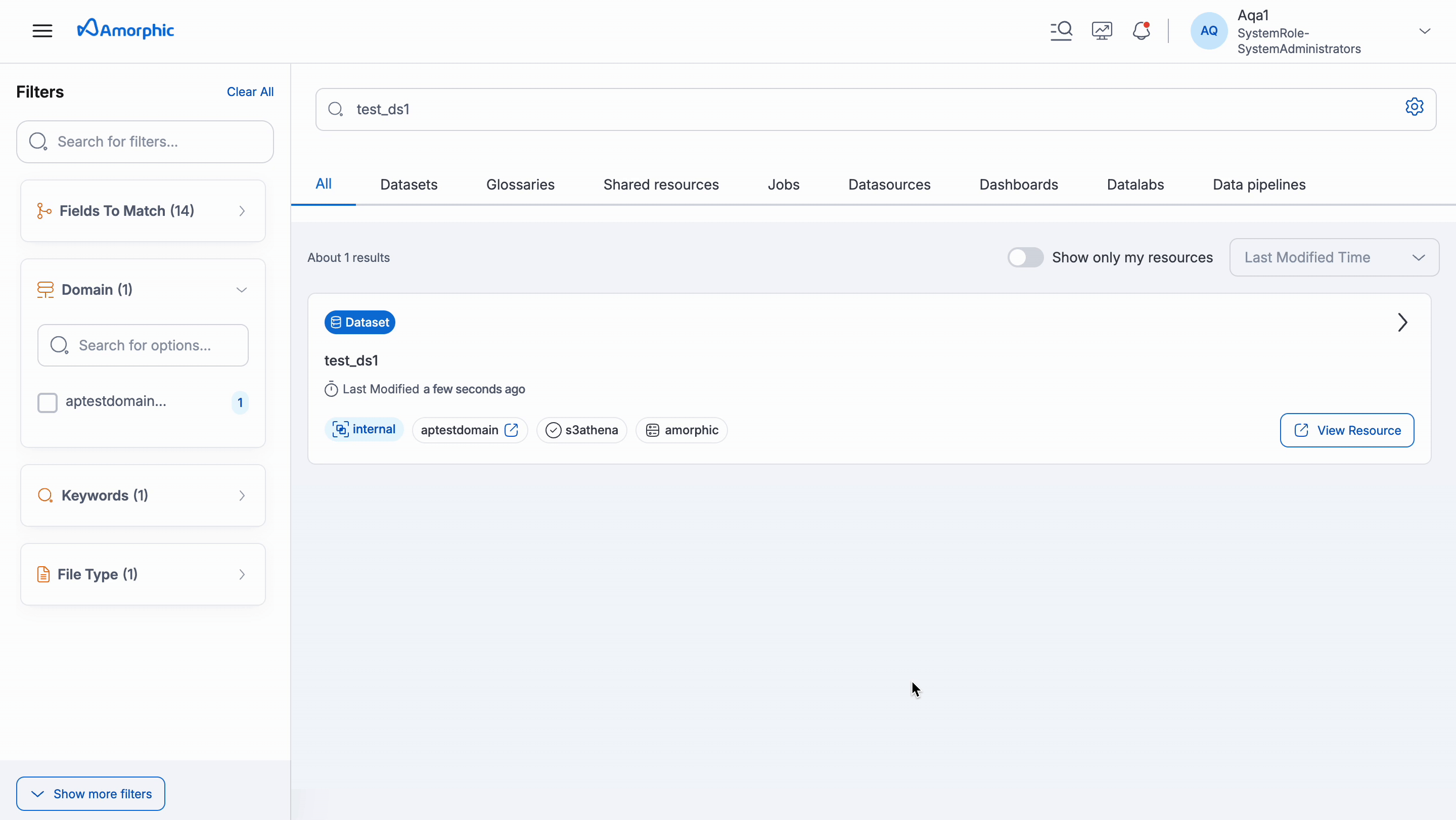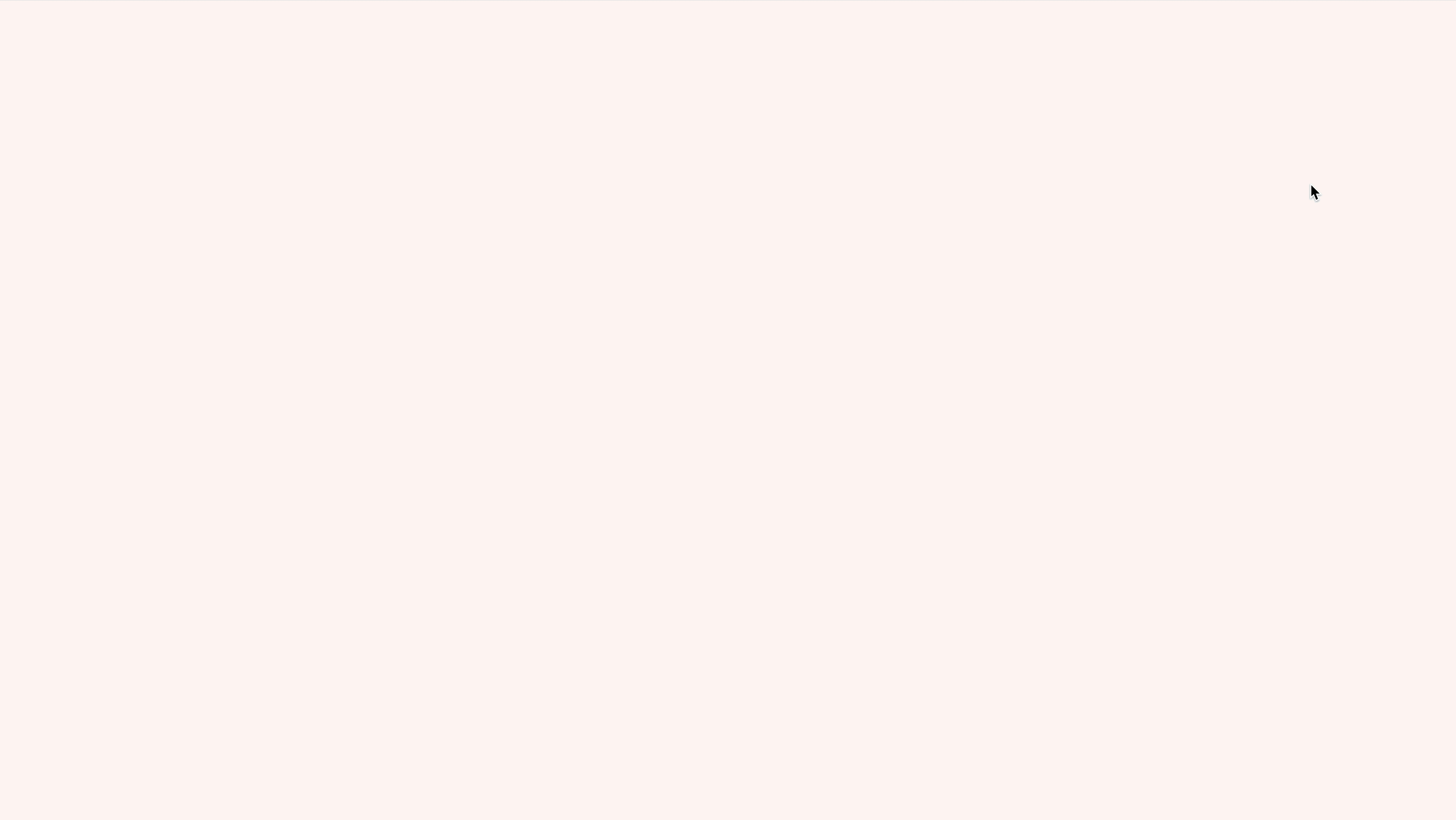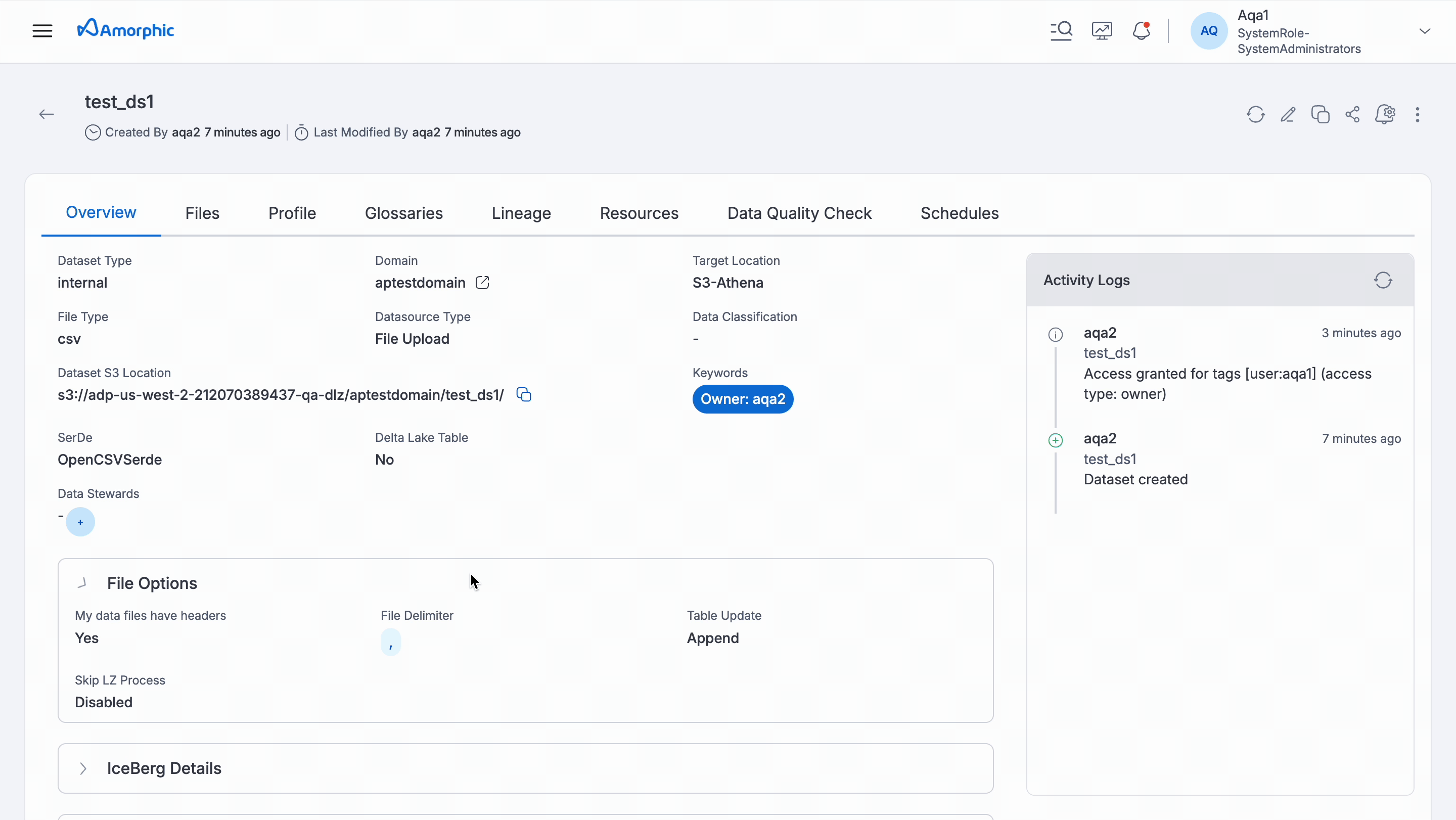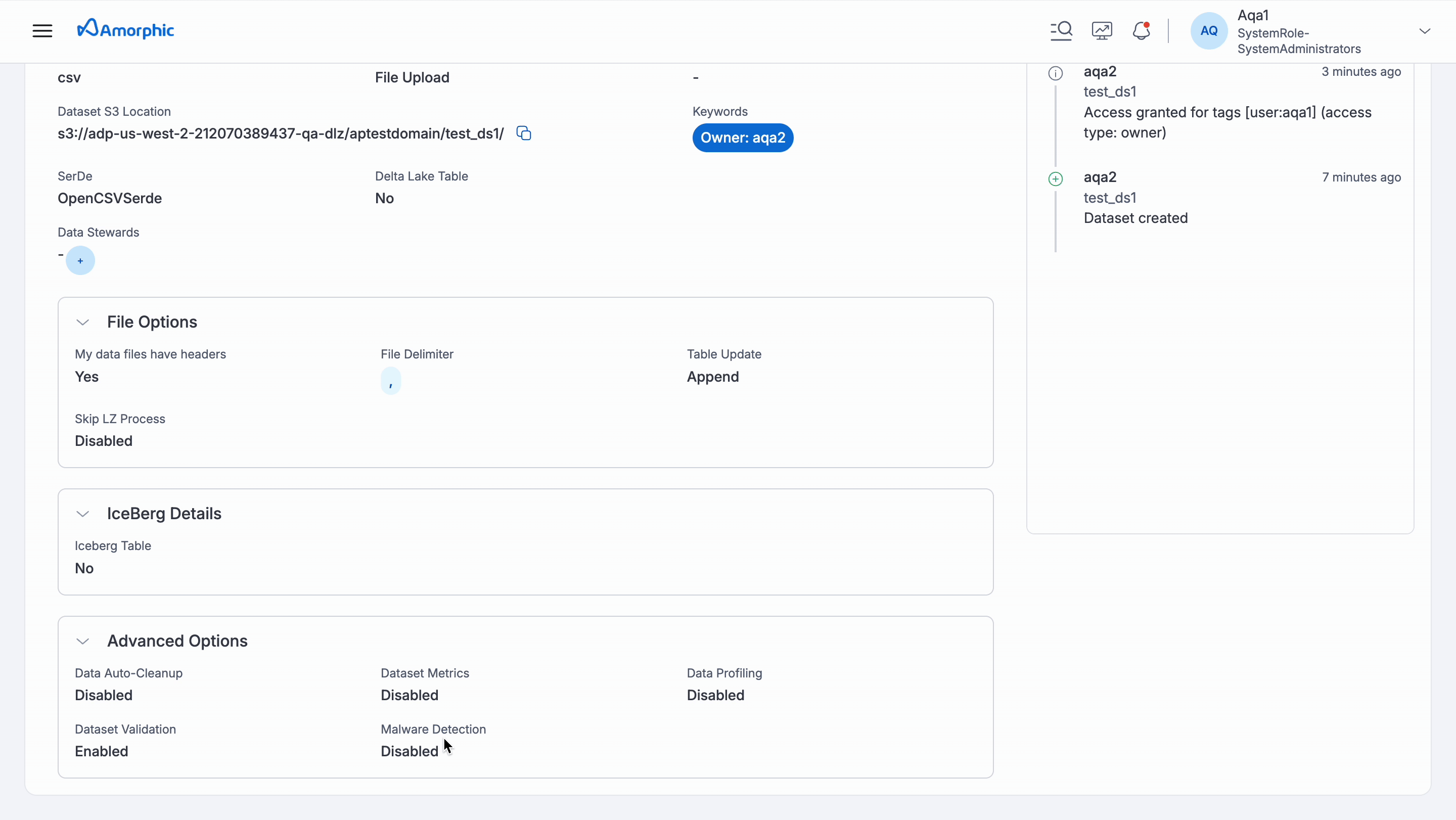
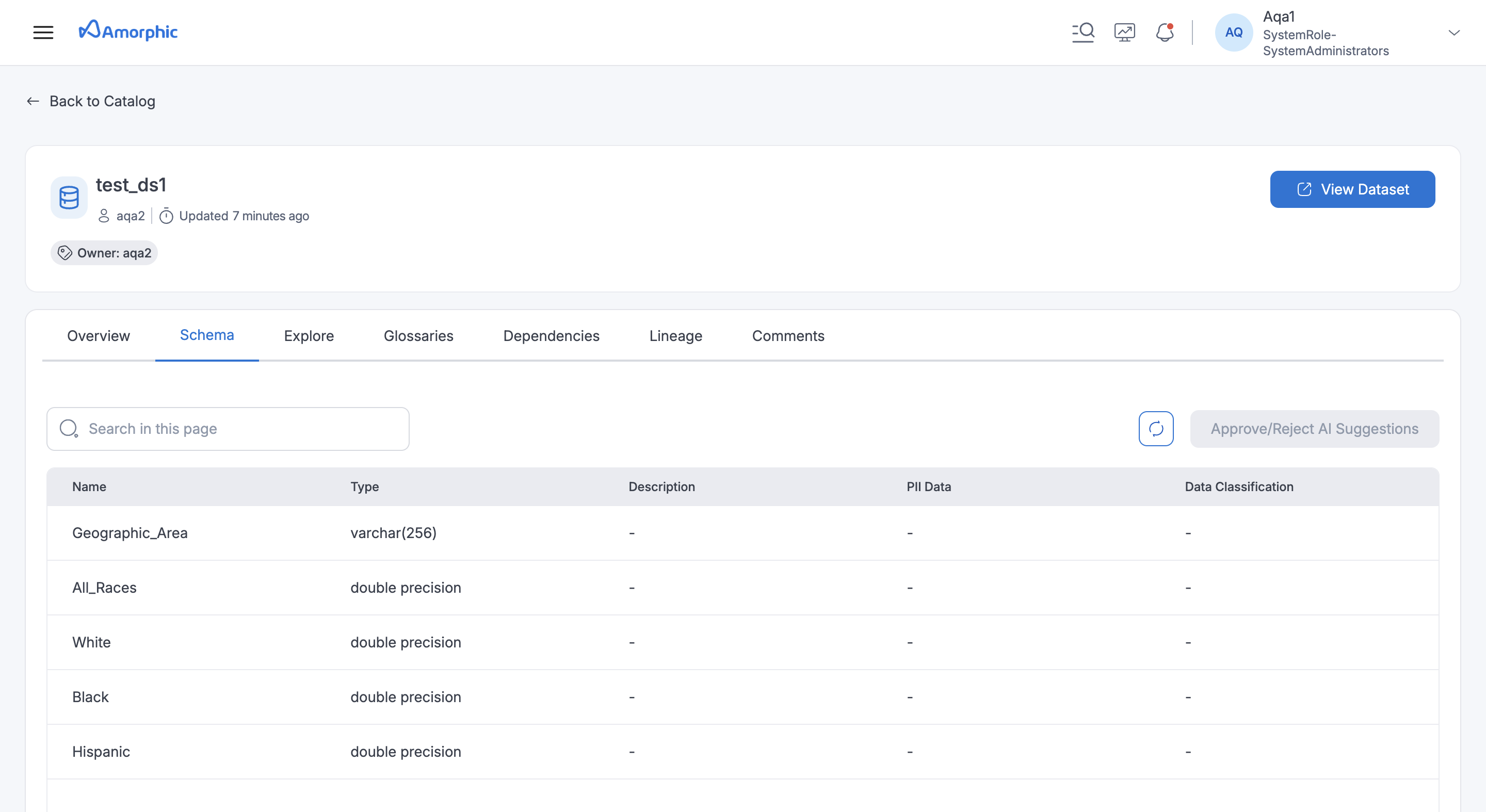
Schema: If user has access, they can view the columns (fields) available in datasets. This helps user understand the structure of the data.
-
AI Suggestions: Amorphic uses AI to provide helpful suggestions about the user's data. These suggestions can be found in the Schema section of the asset details.
- Column Descriptions: Get auto-generated one-liner descriptions that explain what kind of data is stored in each column.
- Column Classifications: AI classifies the data within a column, suggesting relevant categories from a list of 50+ options.
- PII (Personally Identifiable Information) Detection: Amorphic detects if a dataset contains PII and classifies it into 250+ categories.
-
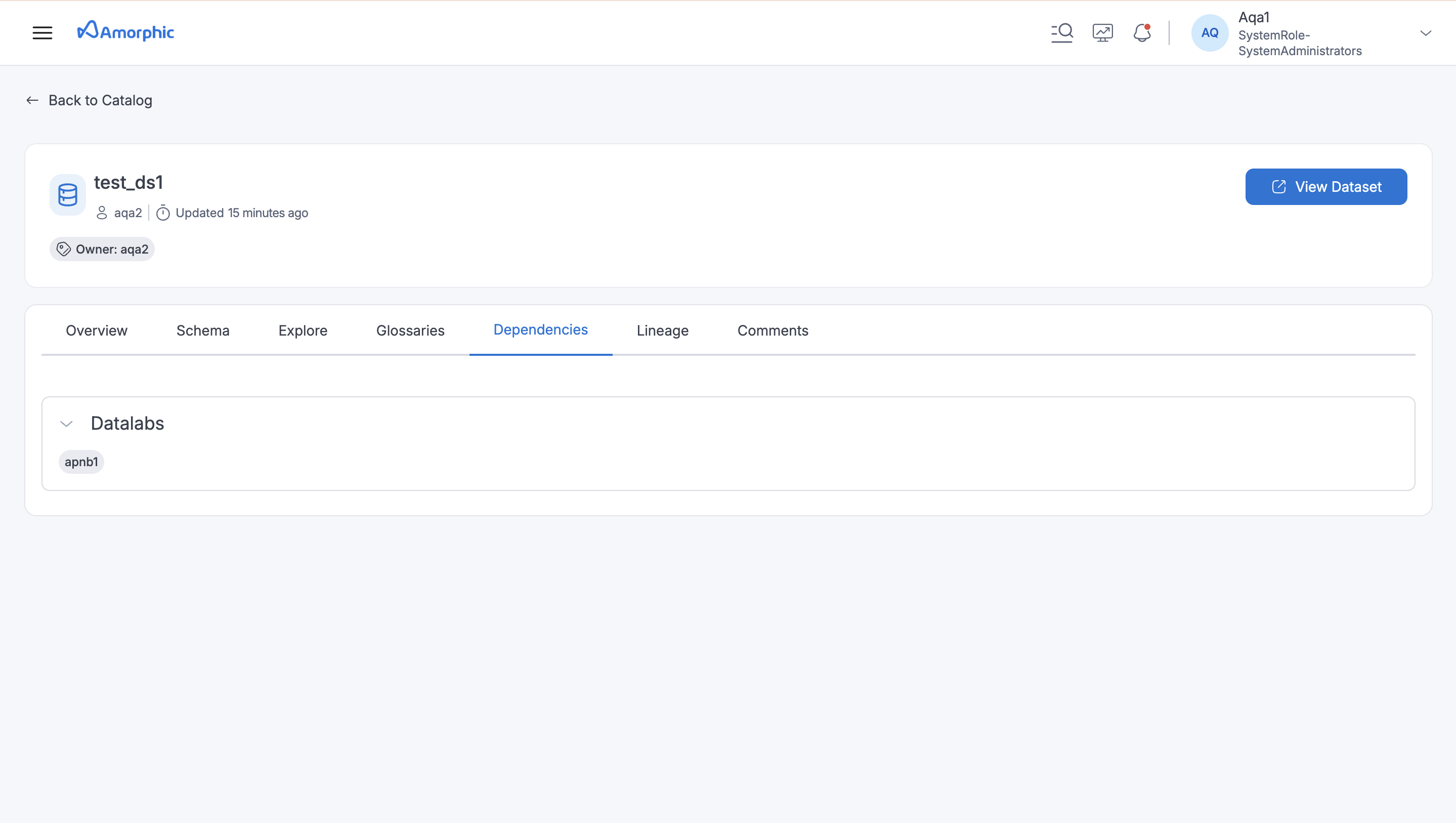
Dependent Resources: Identify resources in Amorphic that rely on specific datasets.
-
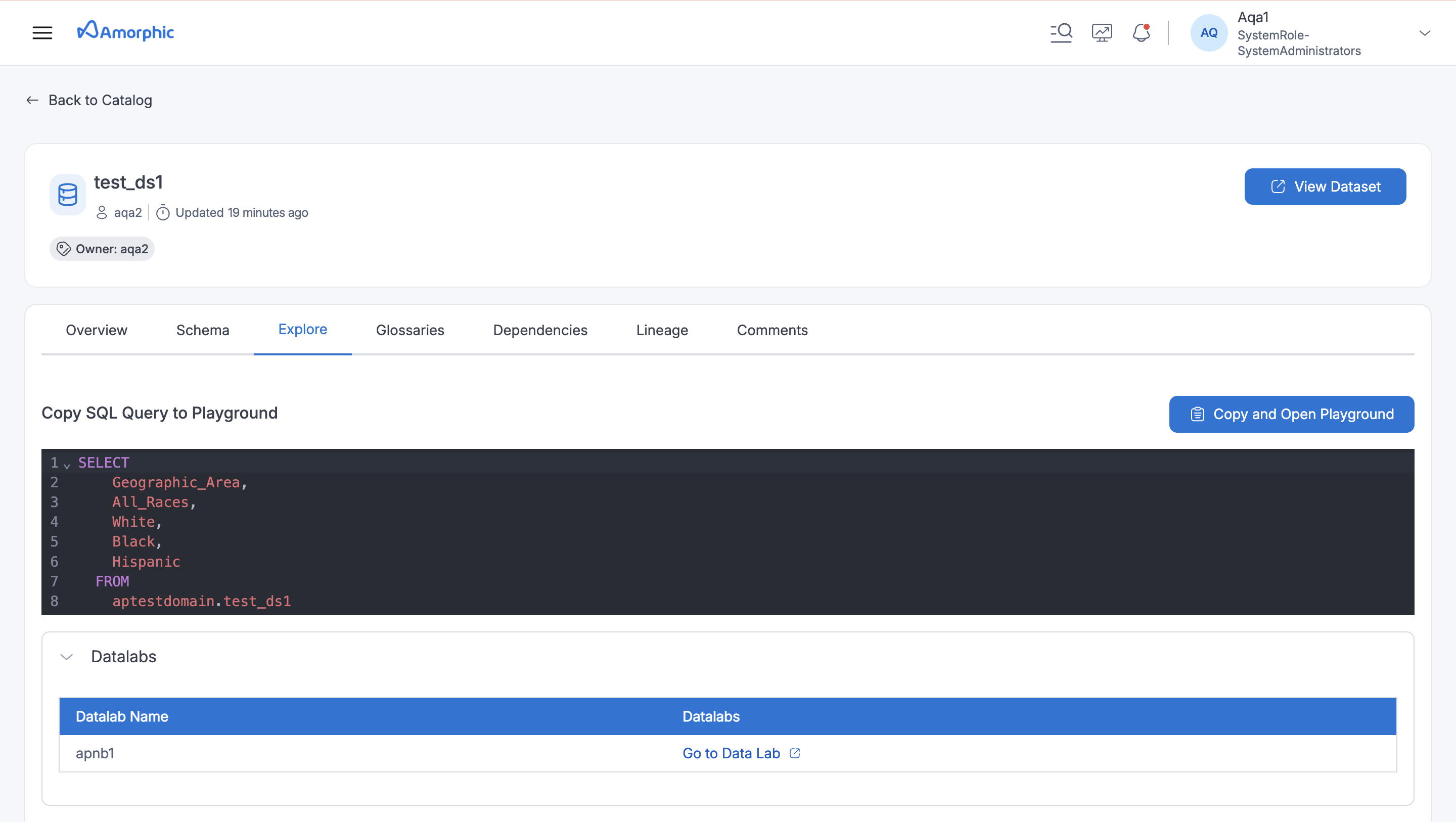
Explore: Access notebooks and studios connected to datasets, allowing user to further investigate the data.
-
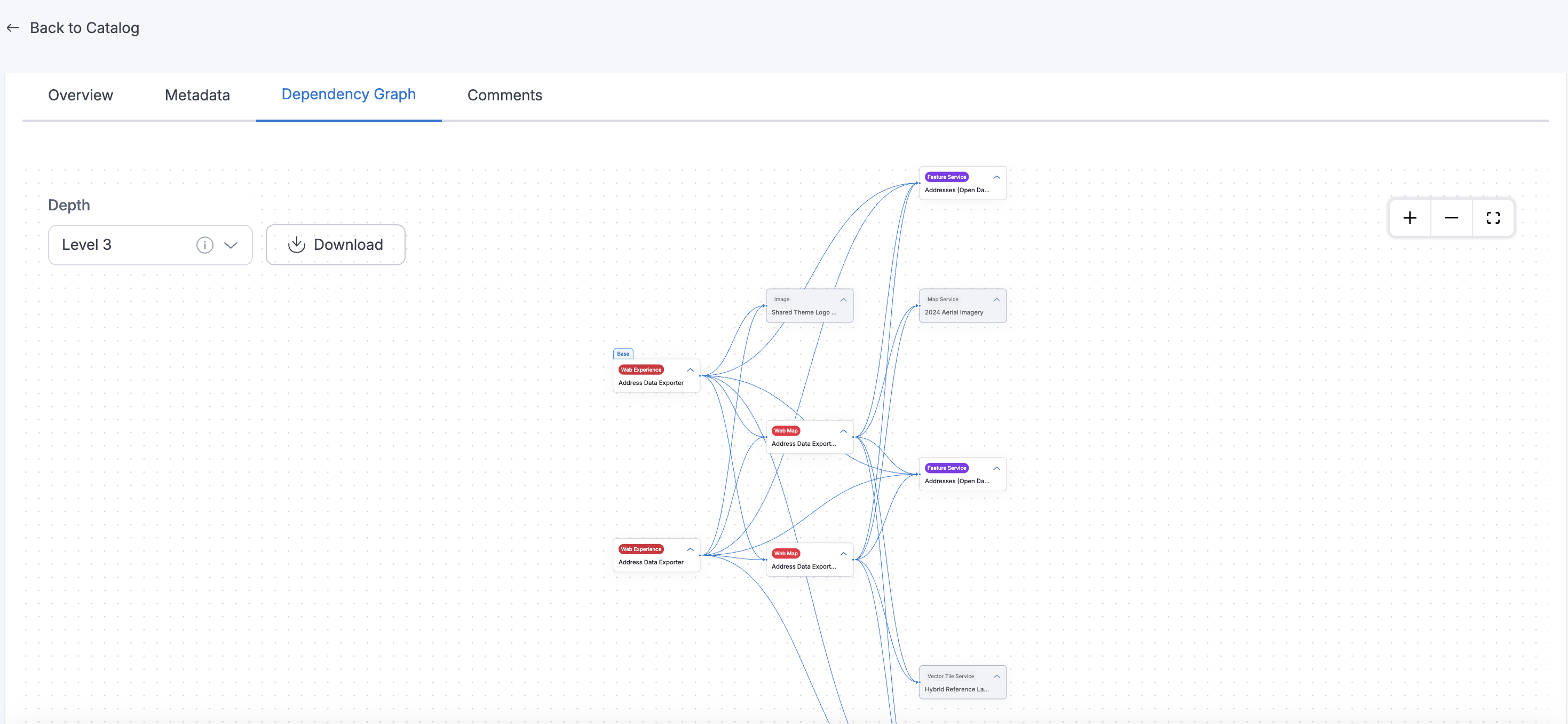
Dependency Graph: provides a visual and interactive way to understand how ArcGIS catalog assets are interconnected within Amorphic. This feature is available exclusively for ArcGIS catalog assets and helps users explore relationships among assets such as Hub Site Applications, Hub Pages, Web Maps, Web Experiences, Feature Services, and Dashboards.
Users can select any ArcGIS catalog asset and view its dependencies in a graphical representation, where each node represents an asset and edges denote relationships between them. The graph supports a depth parameter, allowing users to control the number of relationship levels displayed — up to a maximum depth of 500. This enables both high-level and detailed exploration of asset relationships.
Each node in the graph displays the asset name and asset type. Clicking on a node highlights the nodes connections and reveals additional metadata, including:
- Asset ID
- ArcGIS URL (if available)
ArcGIS items that are not part of the connected ArcGIS Amorphic datasource are shown as greyed-out nodes, indicating they are inaccessible or external to the current context.
To support sharing and offline reference, users can also download the Dependency Graph as a PNG image.
Note- The Dependency Graph feature is not available for non-ArcGIS catalog assets.
- The depth parameter determines how many levels of connected assets are shown from the selected starting node — for example, a depth of 1 shows direct connections, while higher depths recursively expand indirect relationships up to the set limit (max 500).
- Inaccessible or external ArcGIS assets are displayed as greyed-out nodes to help users distinguish them from accessible ones.
Working with AI Suggestions
Amorphic offers AI-driven suggestions to help user better understand data. Here's what user needs to know:
- Availability: AI suggestions are available for datasets with Data Profiling enabled and Target Location: S3Athena, Redshift, Lakeformation, and DynamoDB. Data profiling must be run at least once for the dataset.
- Reviewing Suggestions: User can approve or decline AI suggestions for column descriptions and classifications at the column or asset level. Approved suggestions are added to the asset schema and become searchable. Declined suggestions are removed.
- PII Handling: For PII entities, AI continuously monitors data uploads and alerts user upon detection.
- To get auto-generated descriptions, you must configure a default AI model for the Datasets component. We recommend using the Claude 4 Sonnet model for optimal performance. Without it, user can still receive suggestions for PII entities and classifications.
- AI-generated suggestions may not always be perfect. It's user's responsibility to review and approve or decline them.
- Once approved or declined, AI suggestions cannot be regenerated. However, user can still manually edit descriptions from the Dataset Details page (under the Profile section).

How to Use Datasets
Under Datasets, you can select one or multiple datasets to view step-by-step instructions for using it in Playground or for Analytics Tools like Amorphic BI, Tableau, or Power BI.
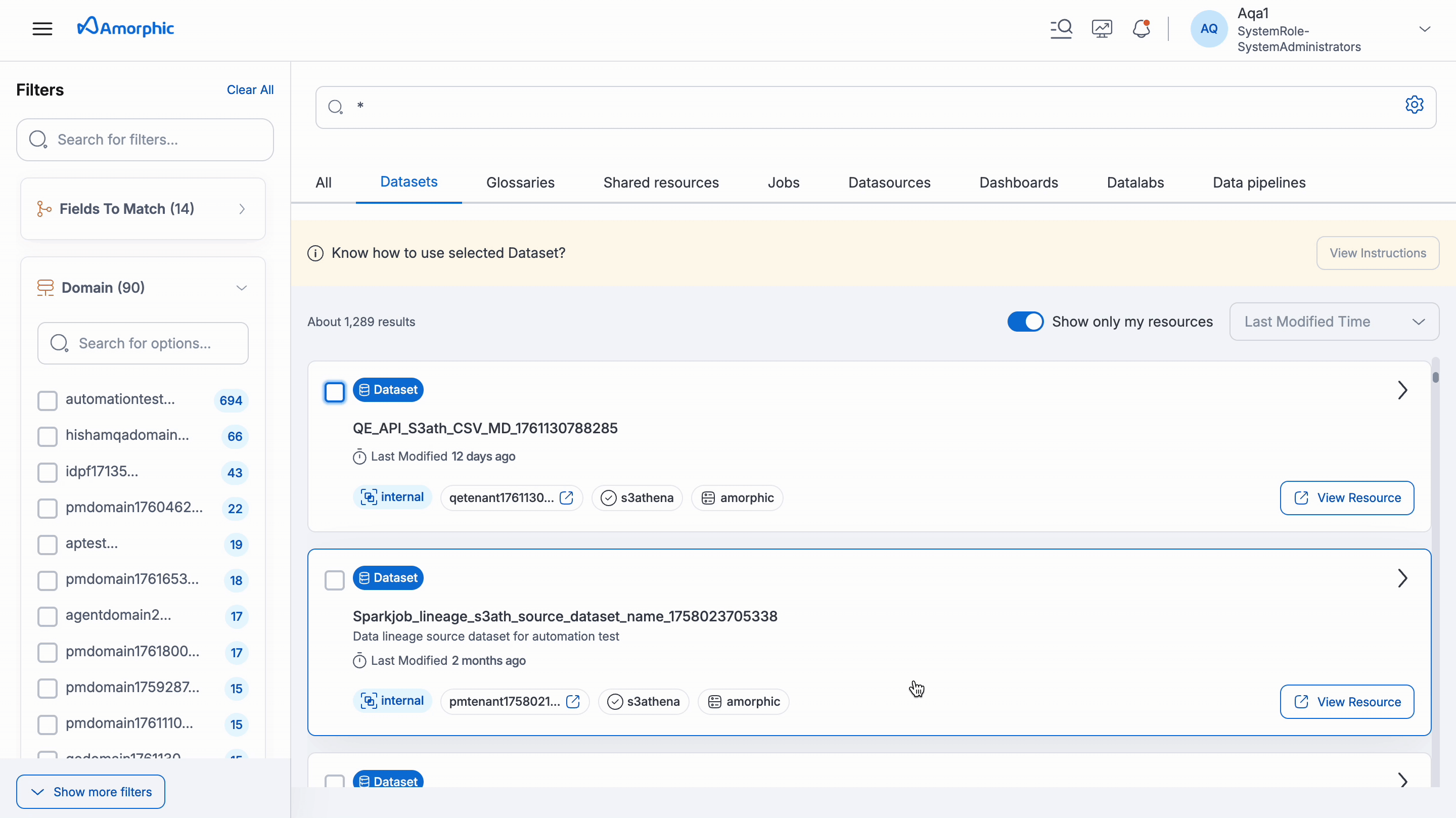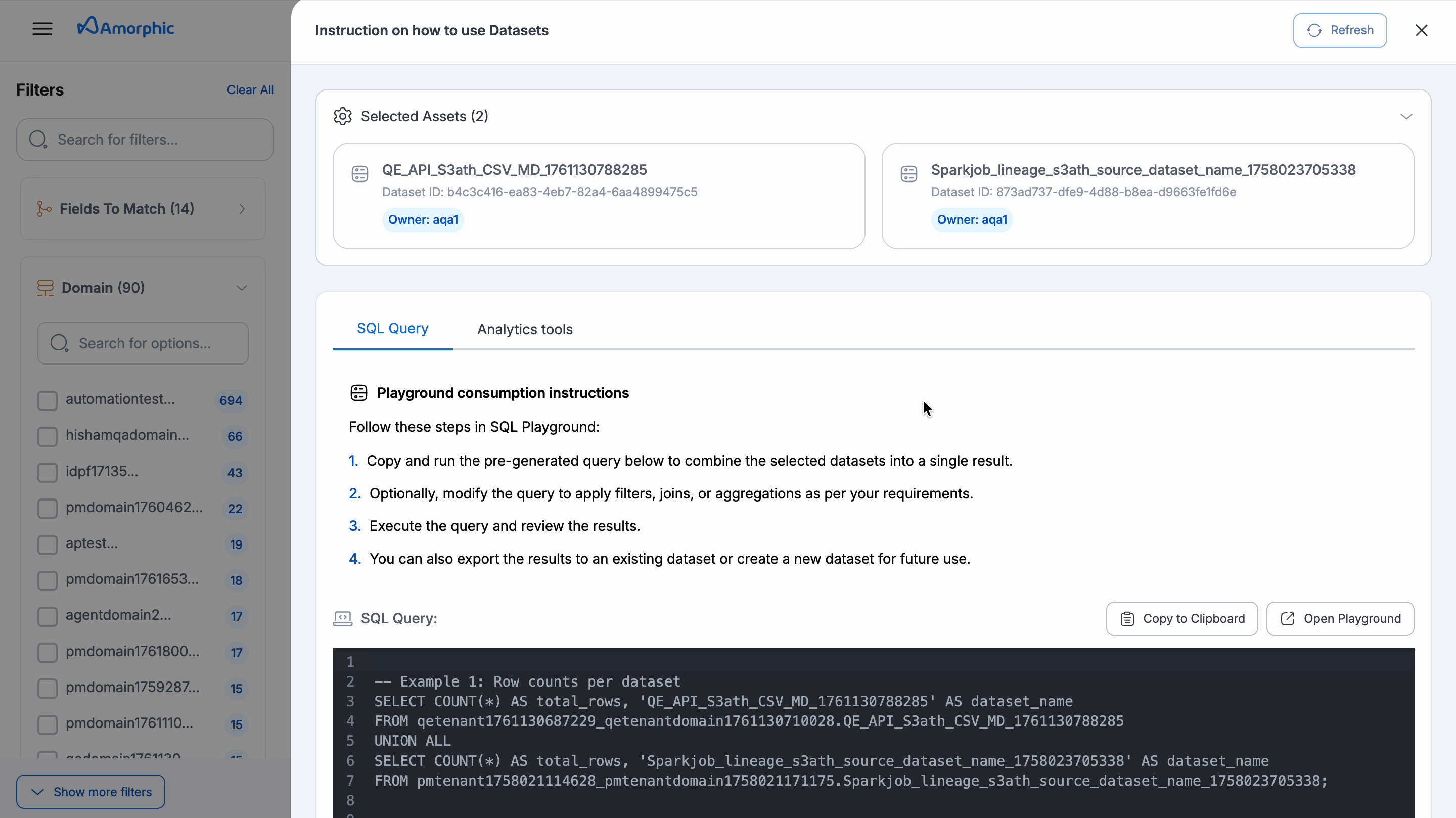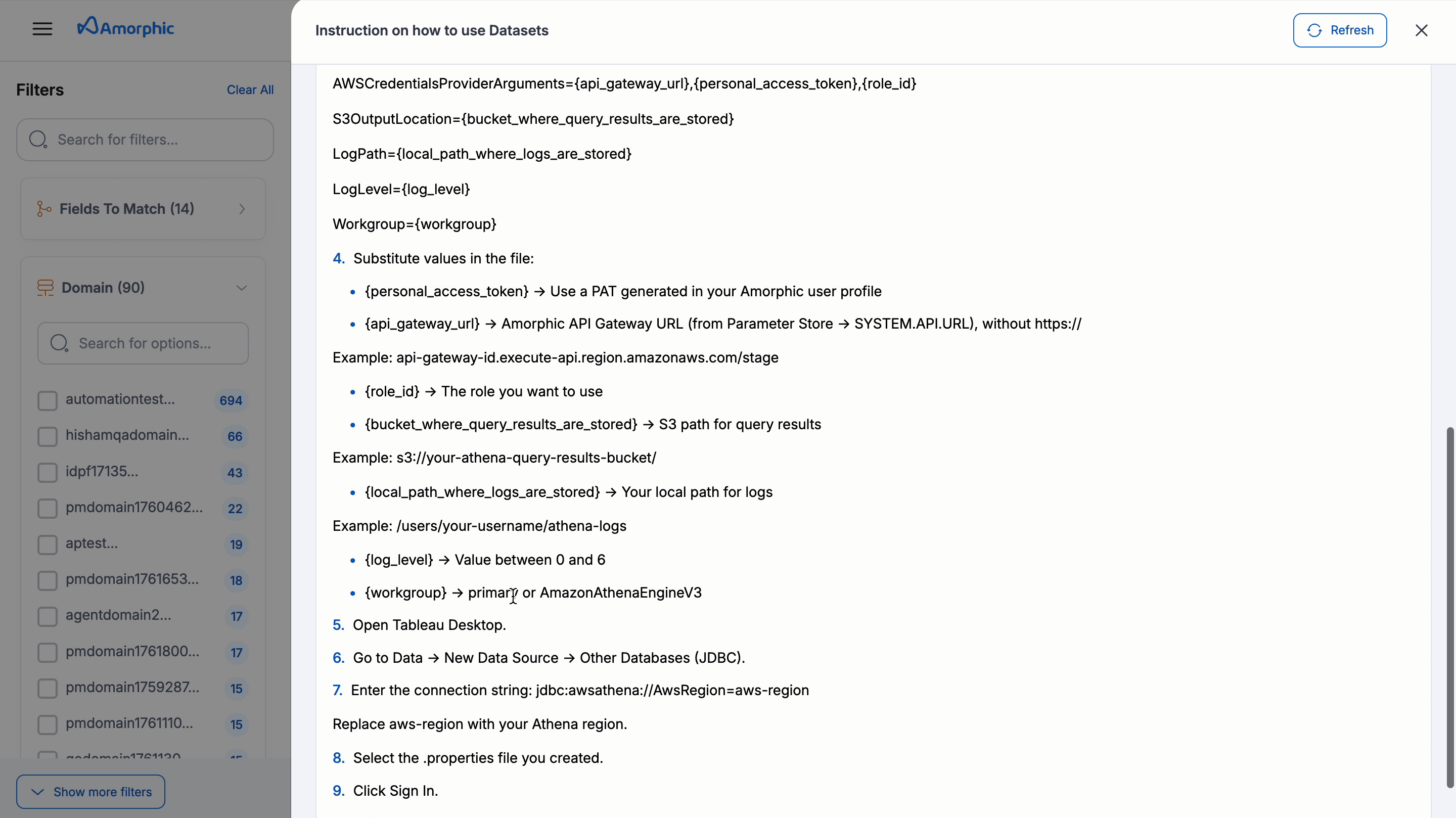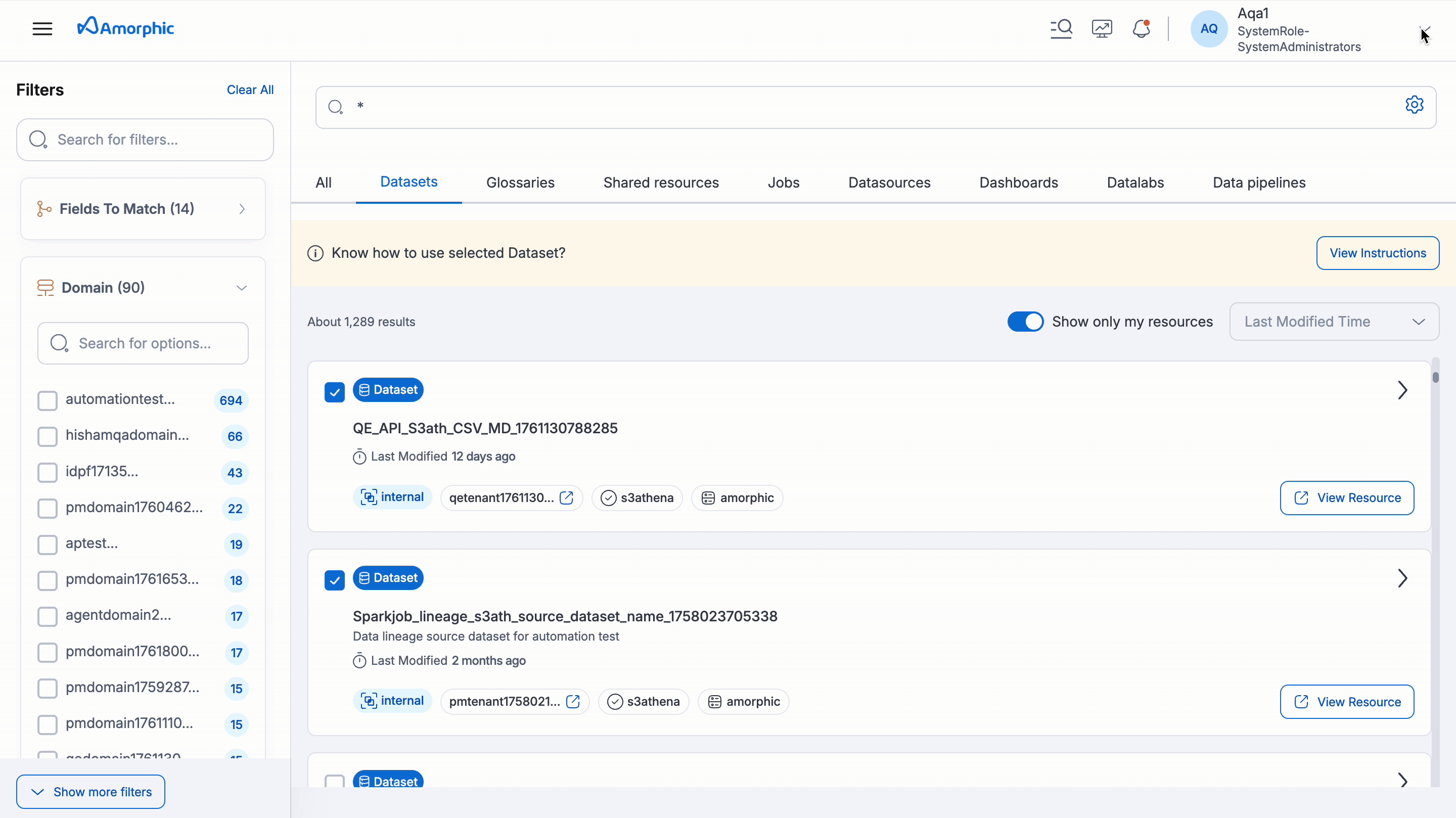
- Instructions are not available for datasets that are unregistered, have an S3 target location, or are inaccessible to the user.
- The sample SQLs provided in the instructions are for guidance and may need editing before successful execution.
- Instructions for Analytical Tool Amorphic BI is only available for user who are registered in it.
Additional Information
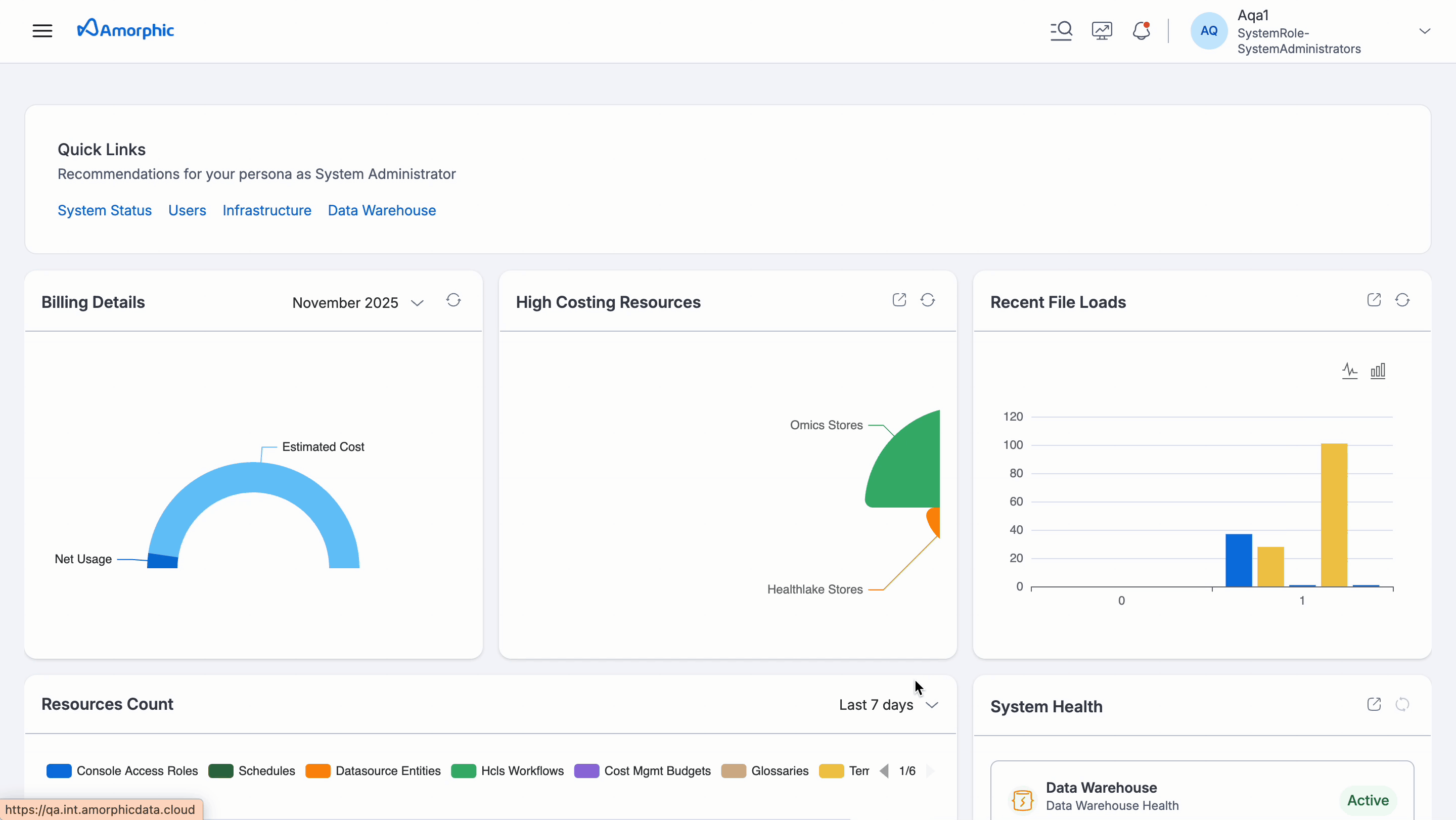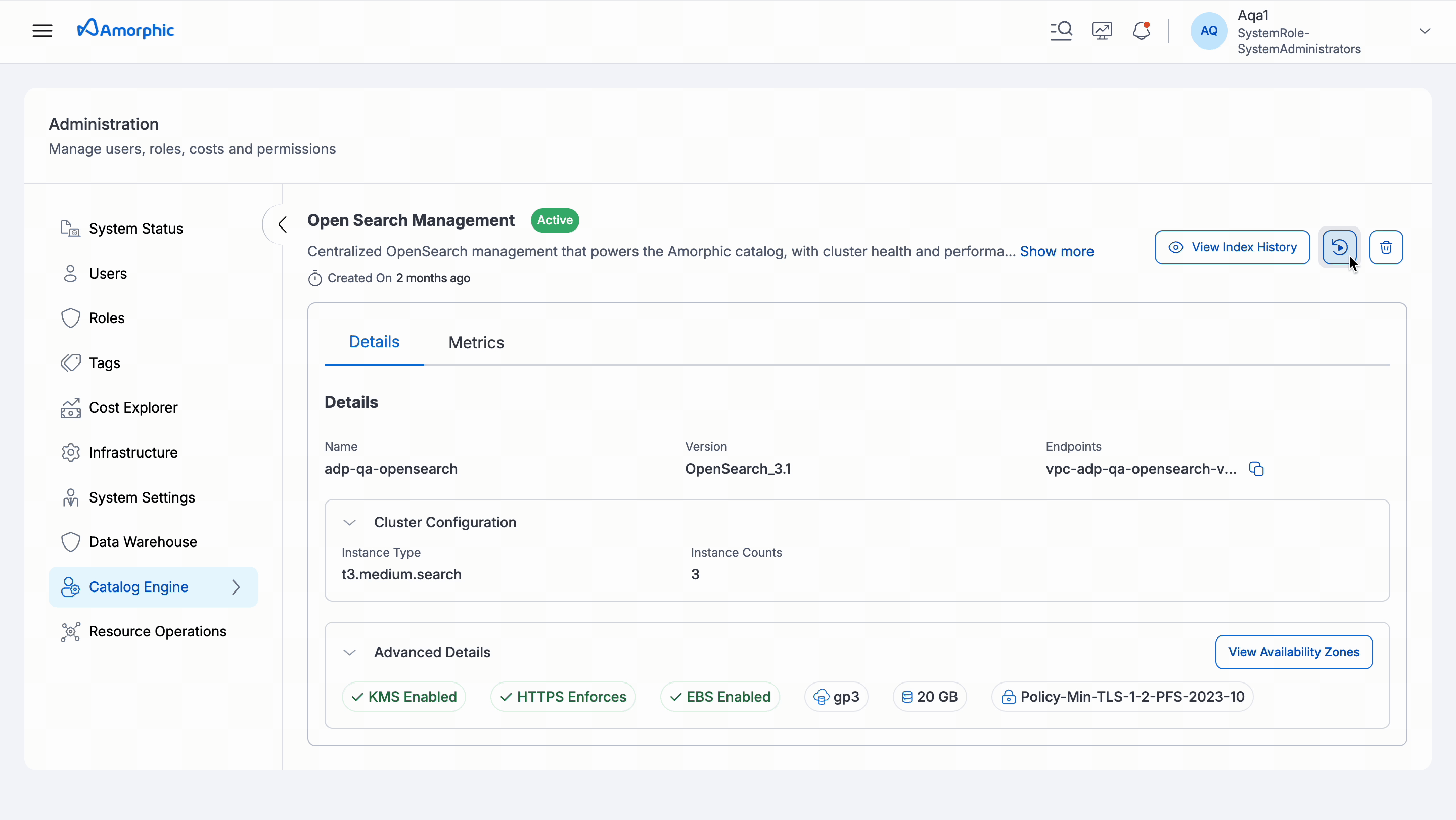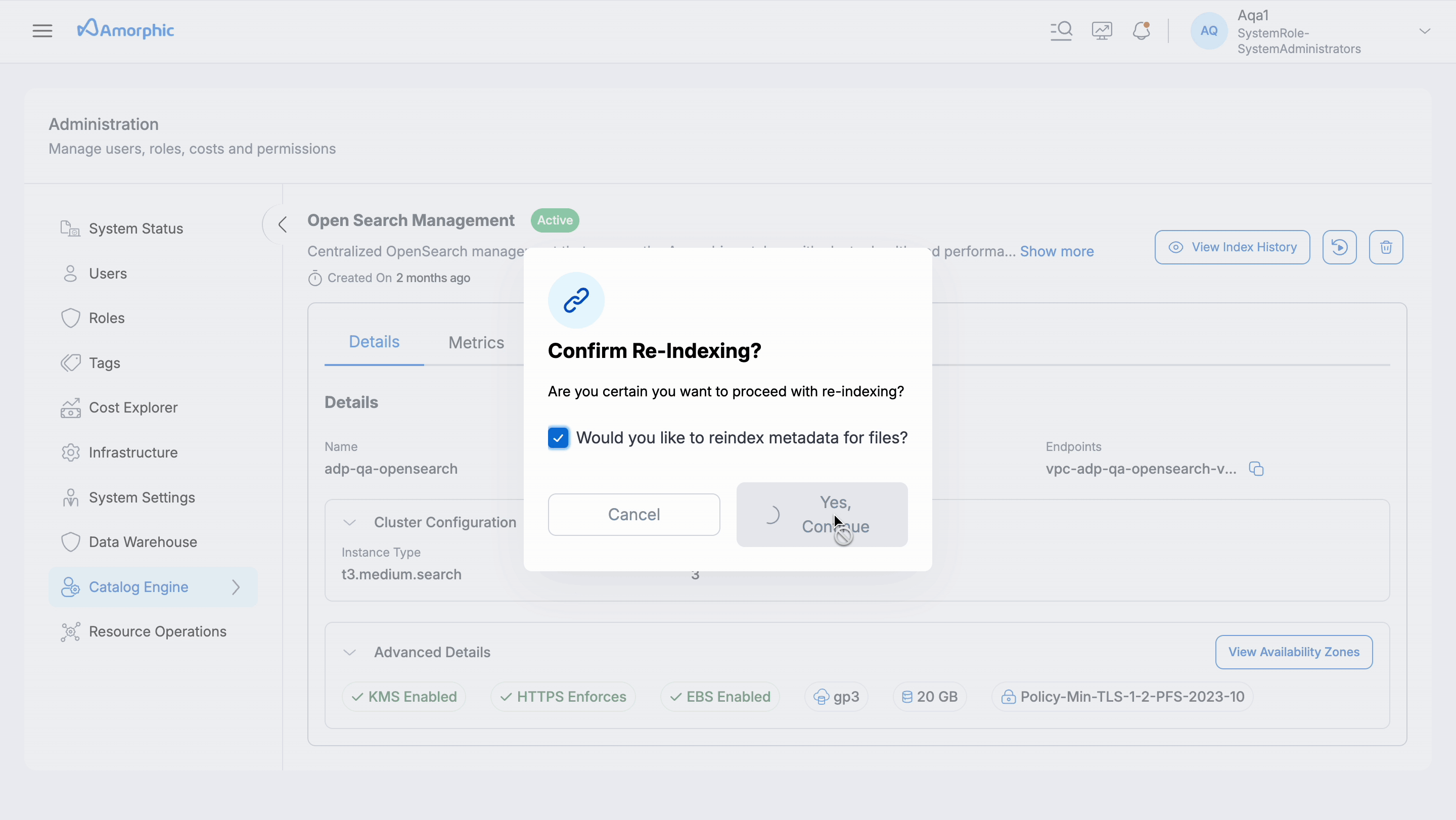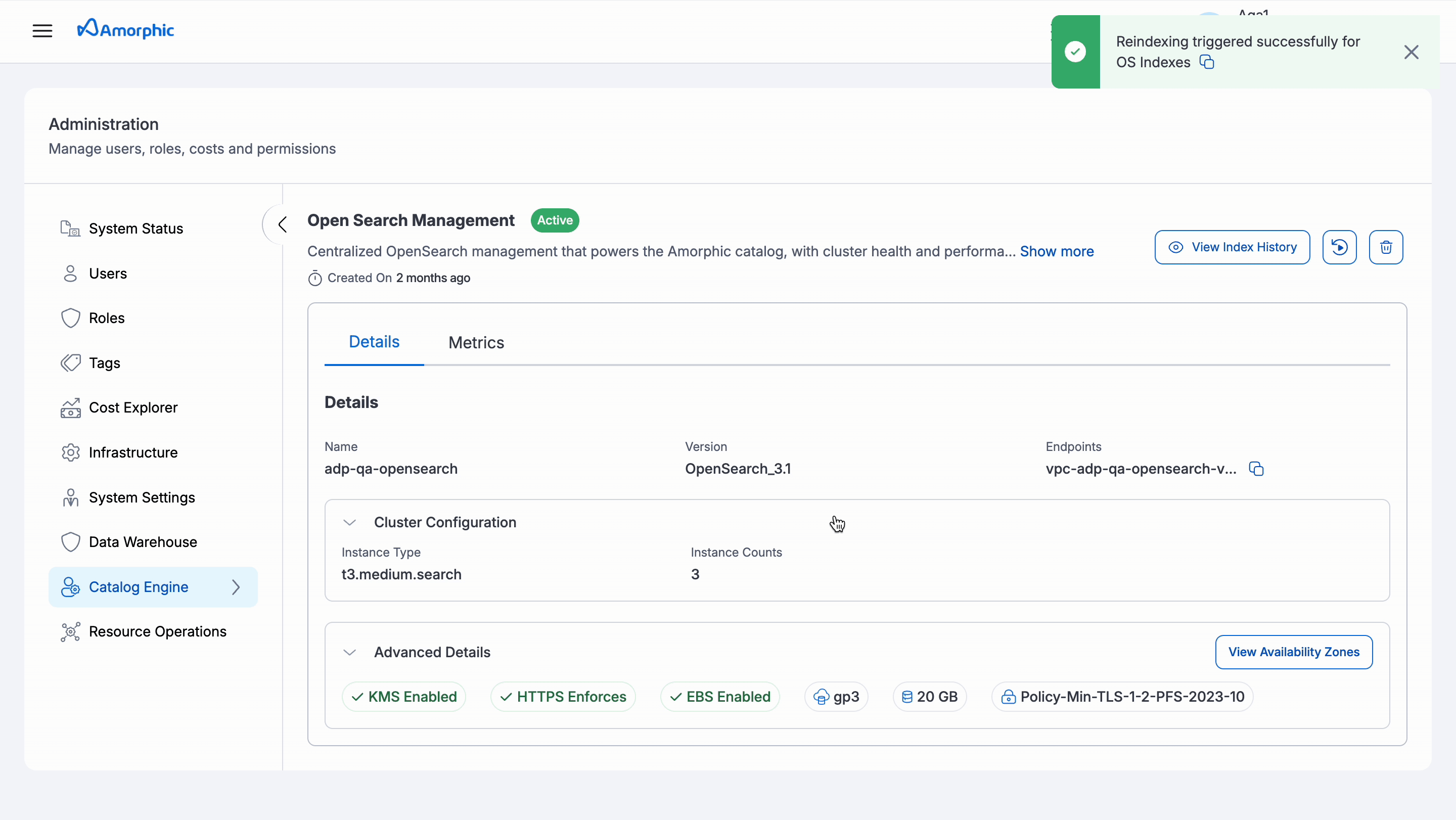
- Repair Catalog Metadata: This feature allows users to repair catalog metadata stored in the indexing cluster. It involves deleting the index and re-indexing the data by reading information from the asset metadata tables. It can be accessed from the OS Management tab in the Administration section.