Agents
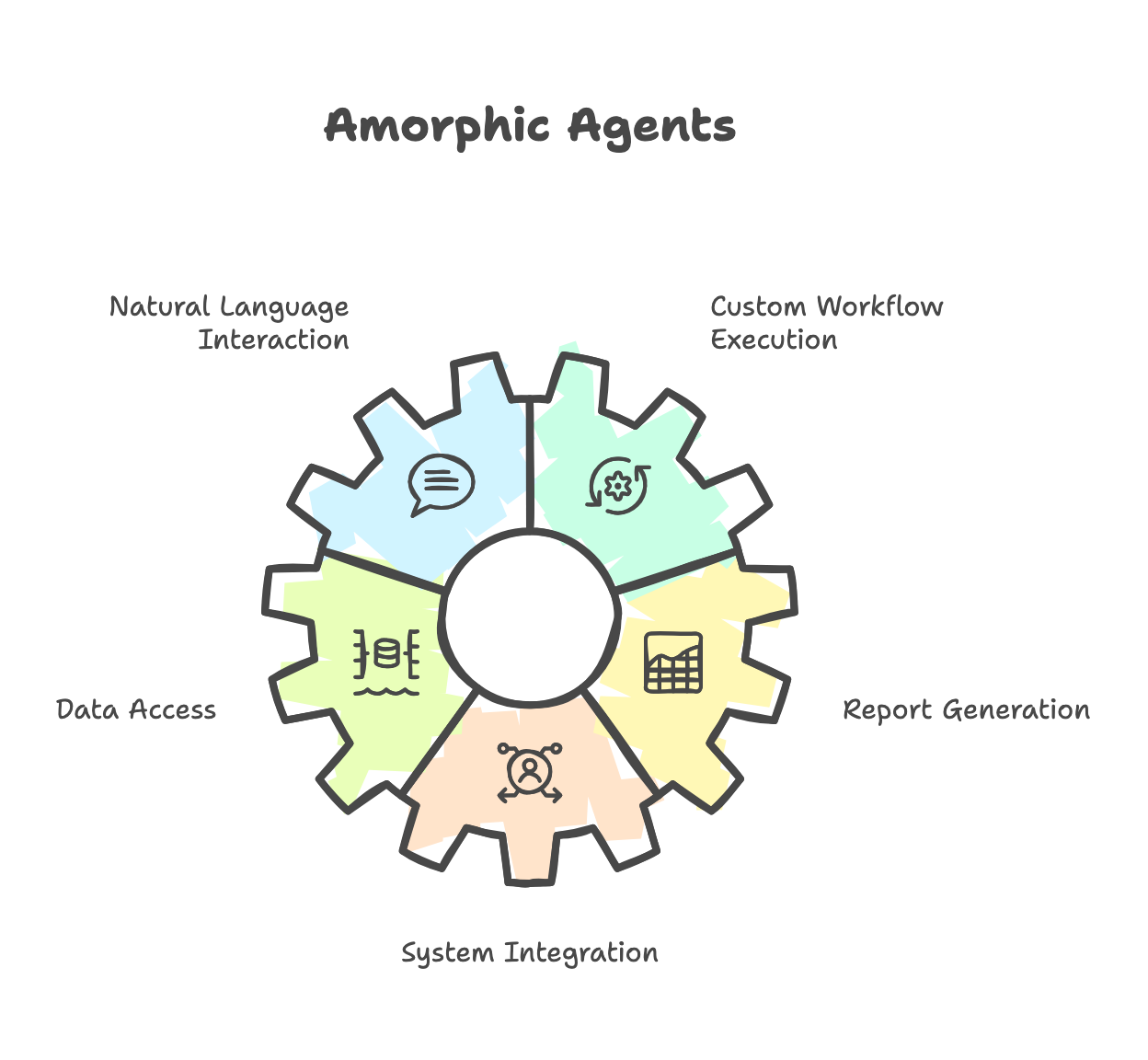
Agents are AI assistants that help you automate workflows and tasks. They understand natural language and can execute custom business processes, making complex operations simple and accessible. Consumption of foundation models with user requirements made easier via Amorphic Agents.
Agents can:
- Chat with users in natural language
- Execute custom workflows and business logic
- Access your data sources and knowledge bases
- Generate reports and insights
- Integrate with external systems and APIs
Agent Operations
Agents can be found under the AI Space of Amorphic. Upon landing on the agents page, users will be able to view all currently deployed/usable agents. Furthermore, Amorphic Agents support following operations:
- Create Agent: Create a new agent
- View Agent: View the agent details
- Edit Agent: Edit the agent to add more tools or update metadata
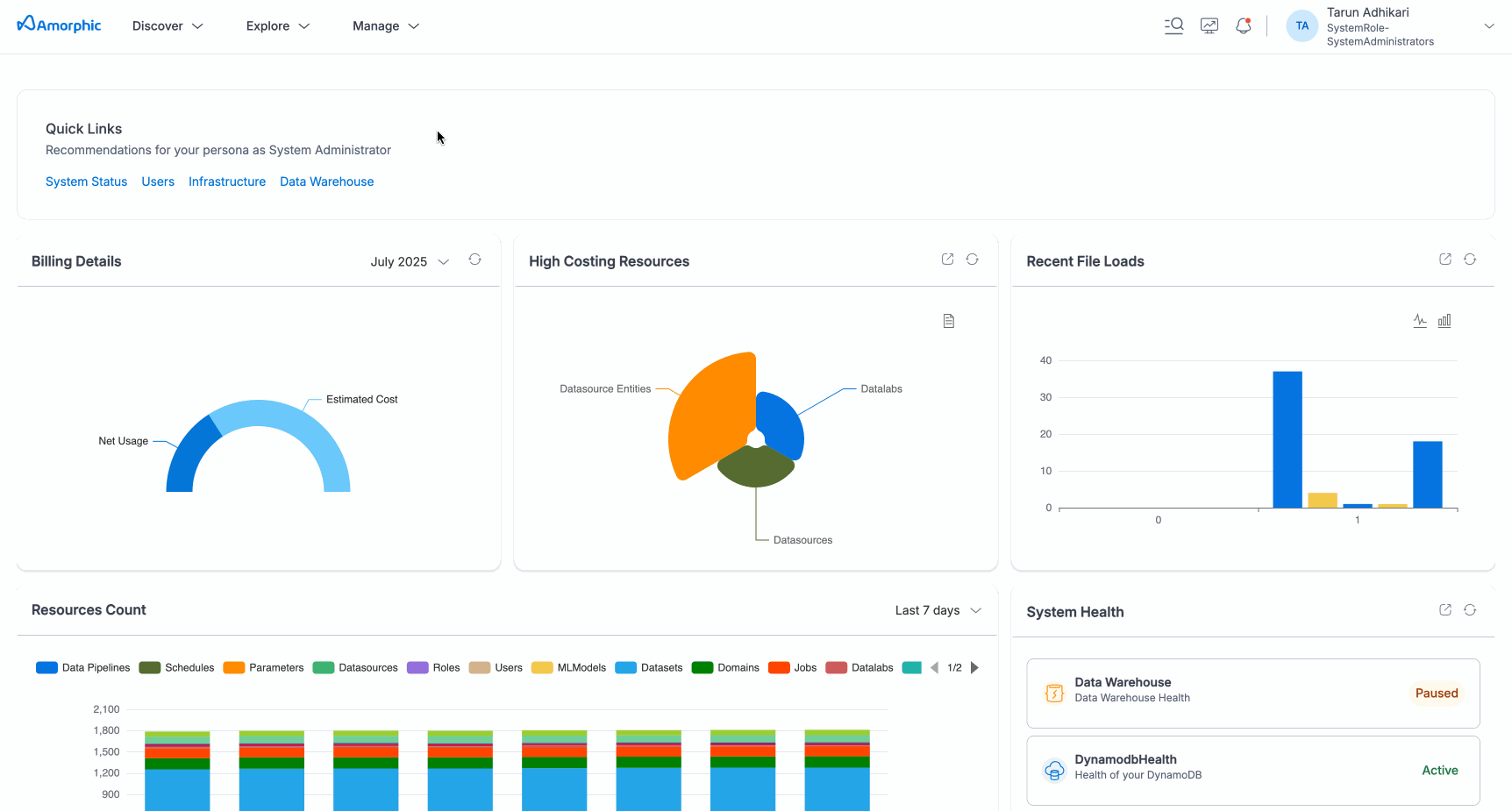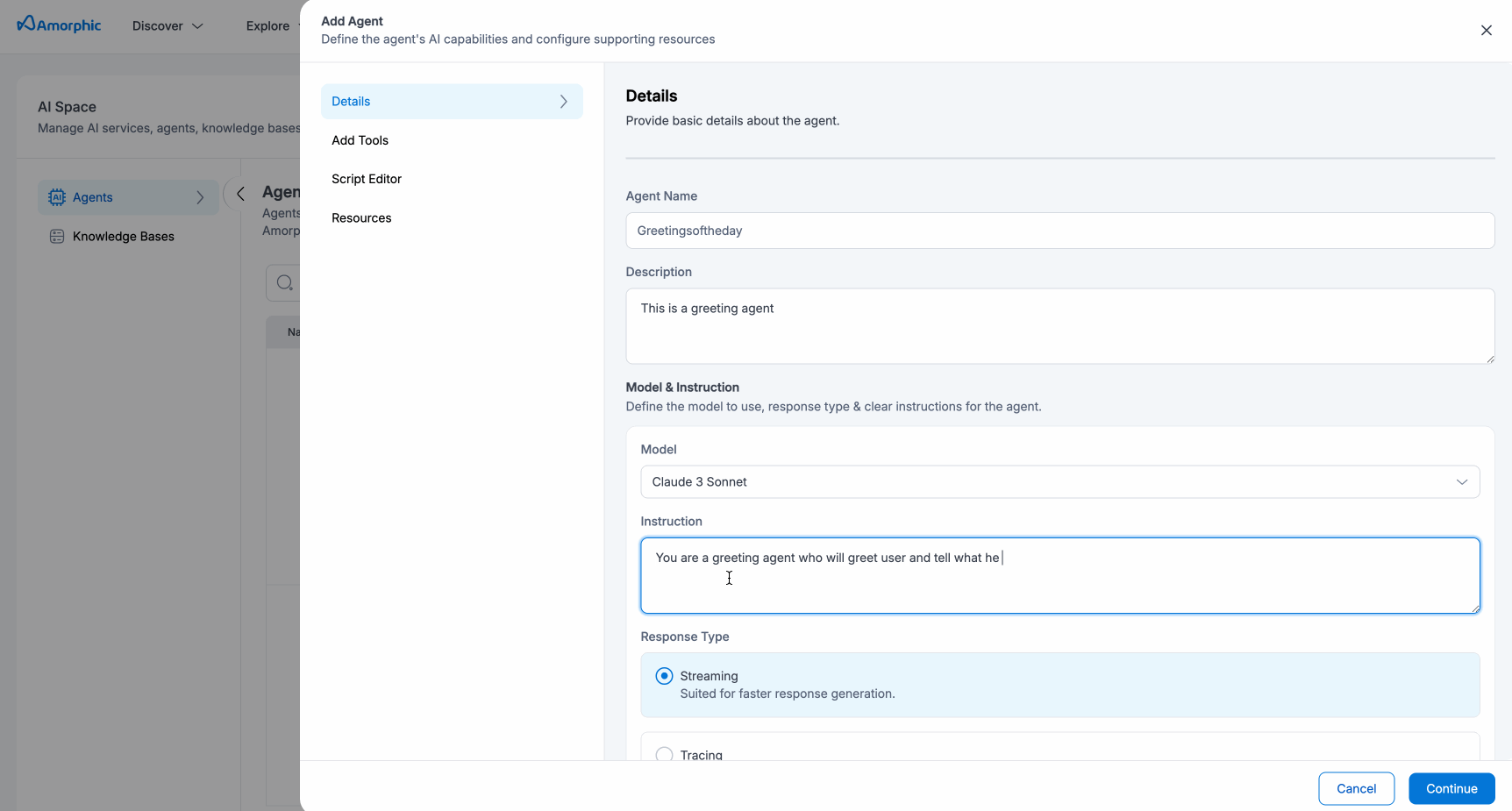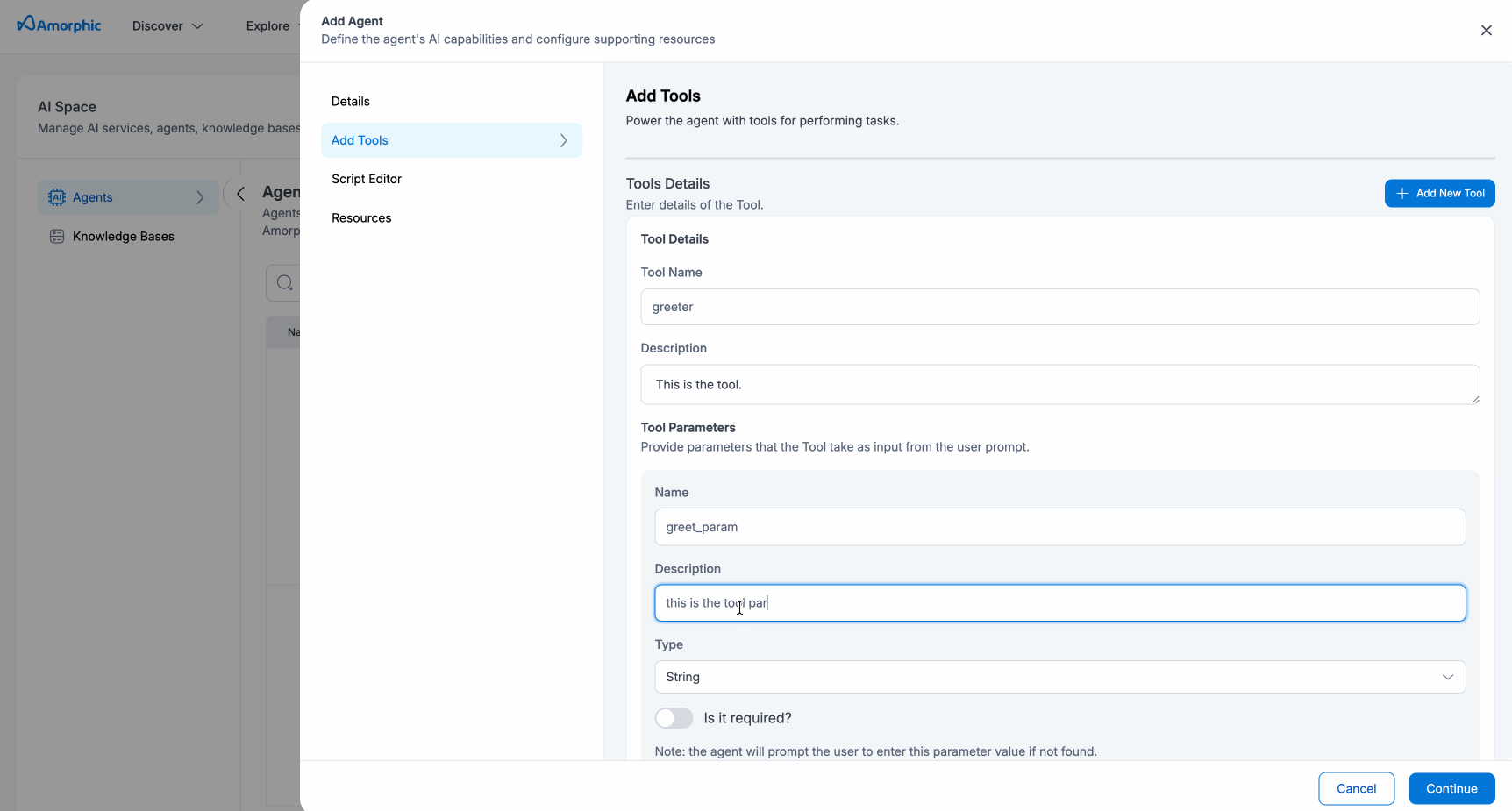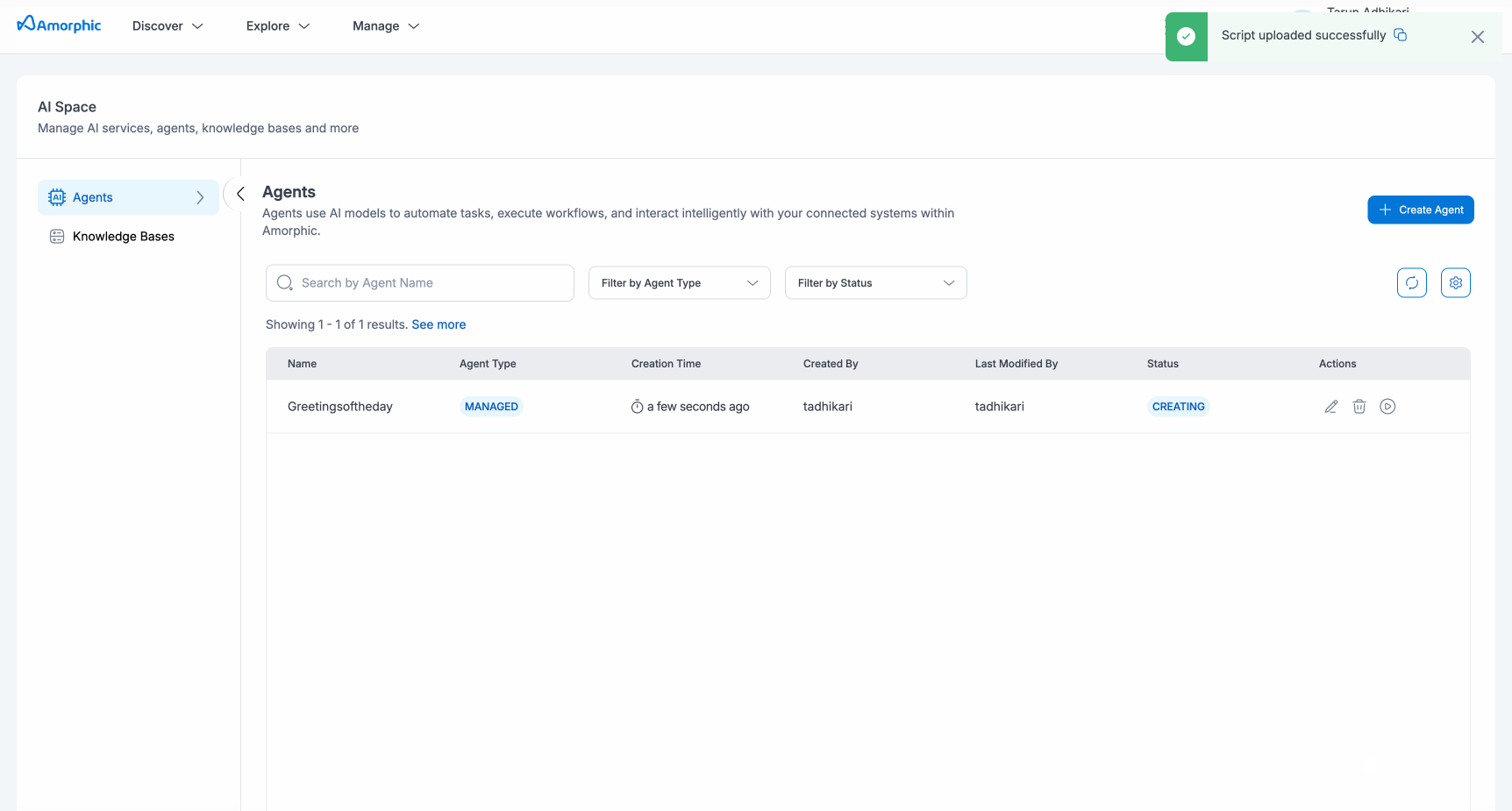
Create Agent
- Go to Explore > AI Space > Agents
- Click Create Agent
- Fill in the following information:
- Agent Name: Choose a descriptive name
- Description: Brief explanation of what the agent does
- Model: Select an AI model
- Instructions: Tell the agent what to do (minimum 40 characters)
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Agent Name | The name by which the user wants to create the agent. |
| Description | A brief explanation of what the agent does |
| Model | Select an AI model which is enabled for Amorphic |
| Instructions | Tell the agent what to do (minimum 40 characters), specifying the user's requirements for the agent. |
| Response Type | Users can select either one of the available response types required from the agent: Streaming: Suited for faster response generation Tracing: Helps understand the agent's reasoning process. |
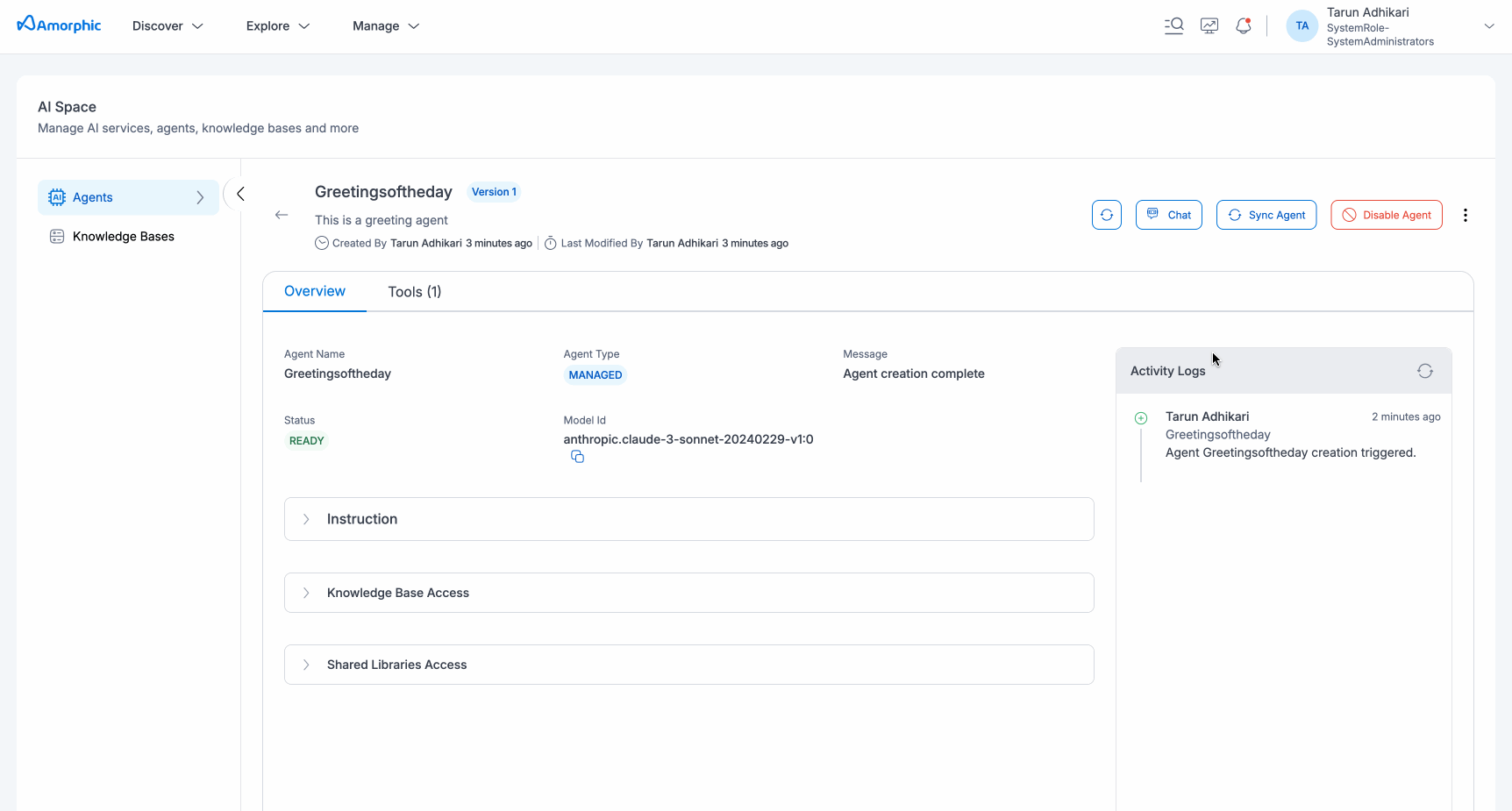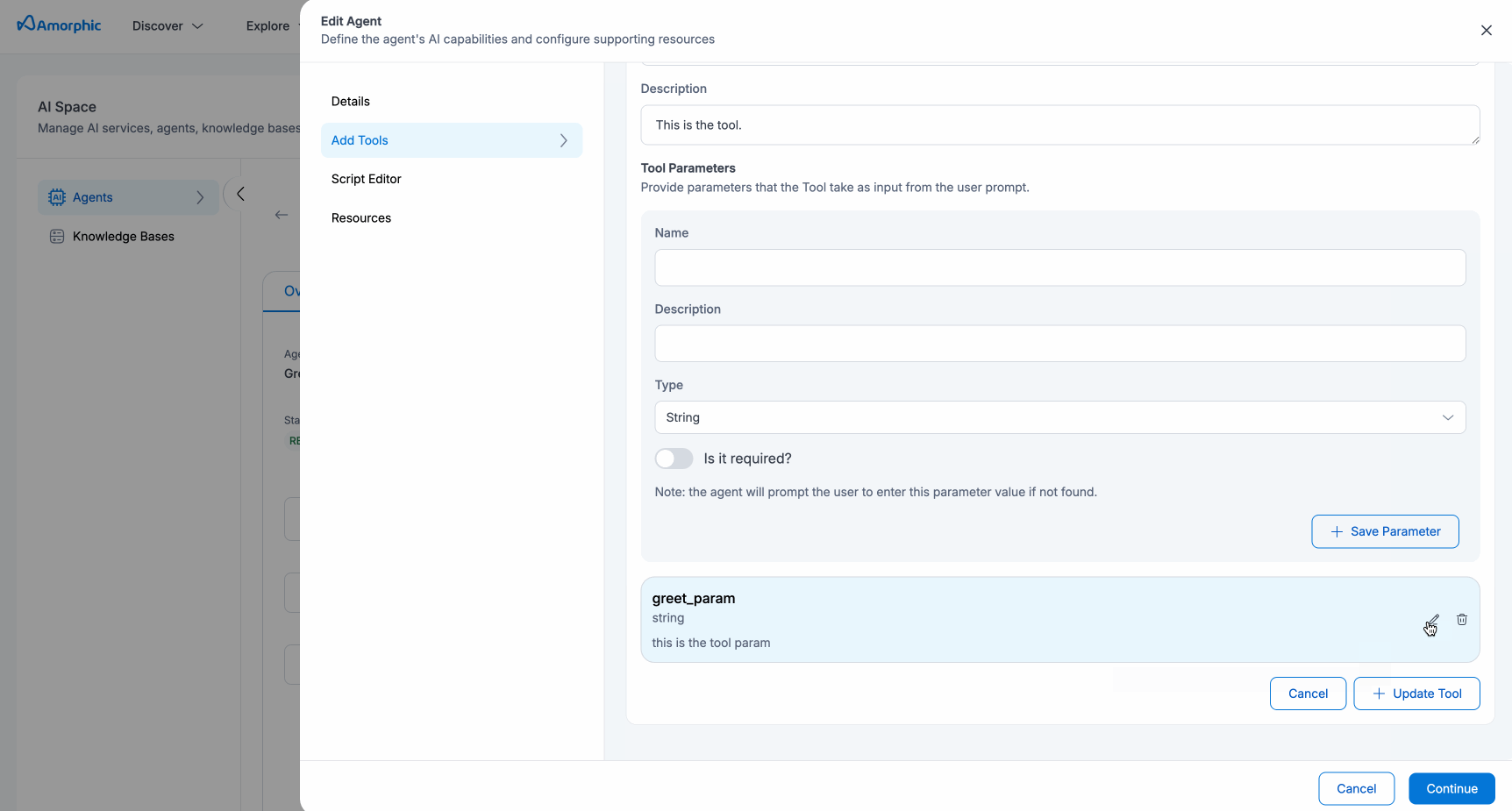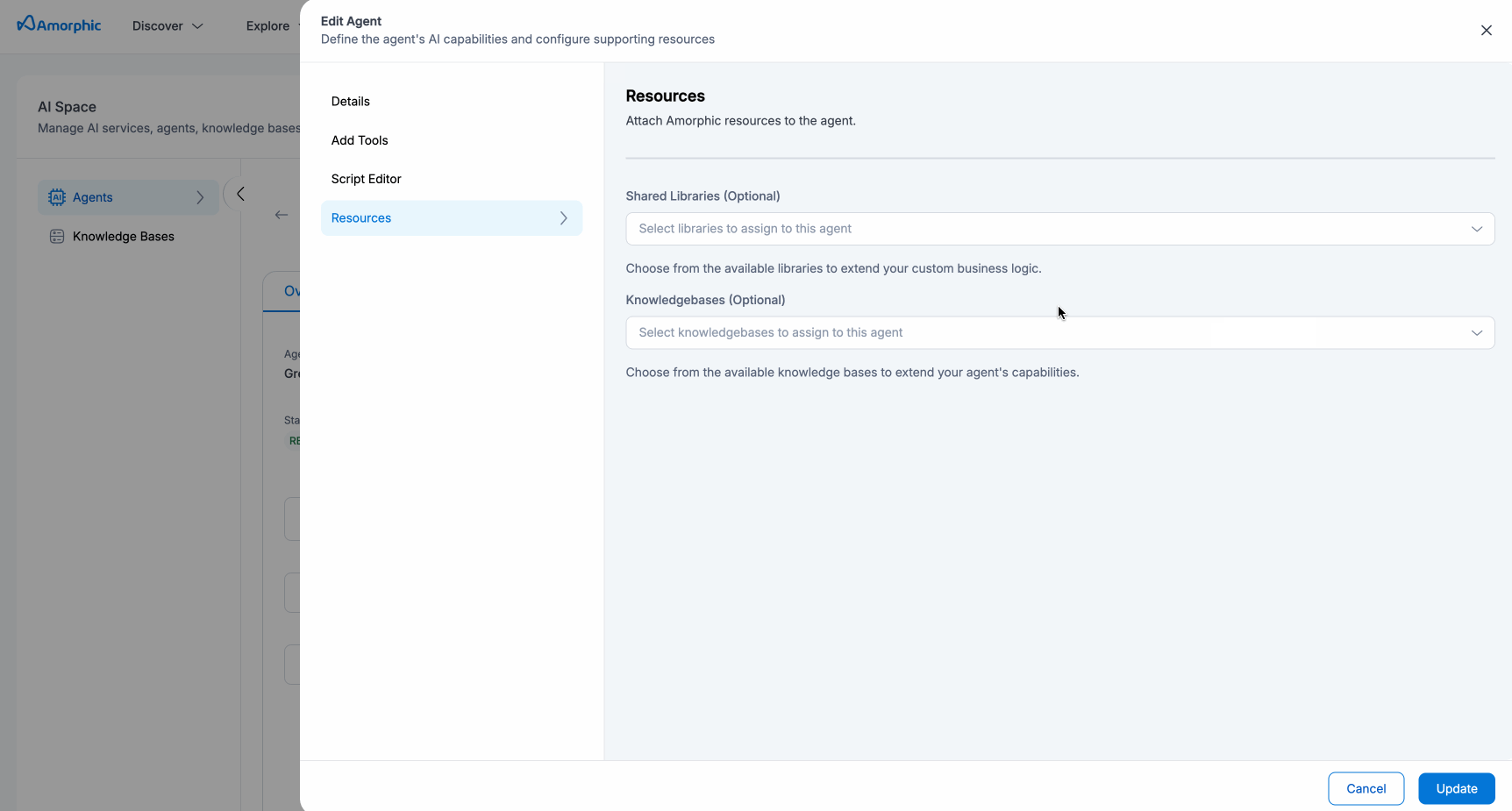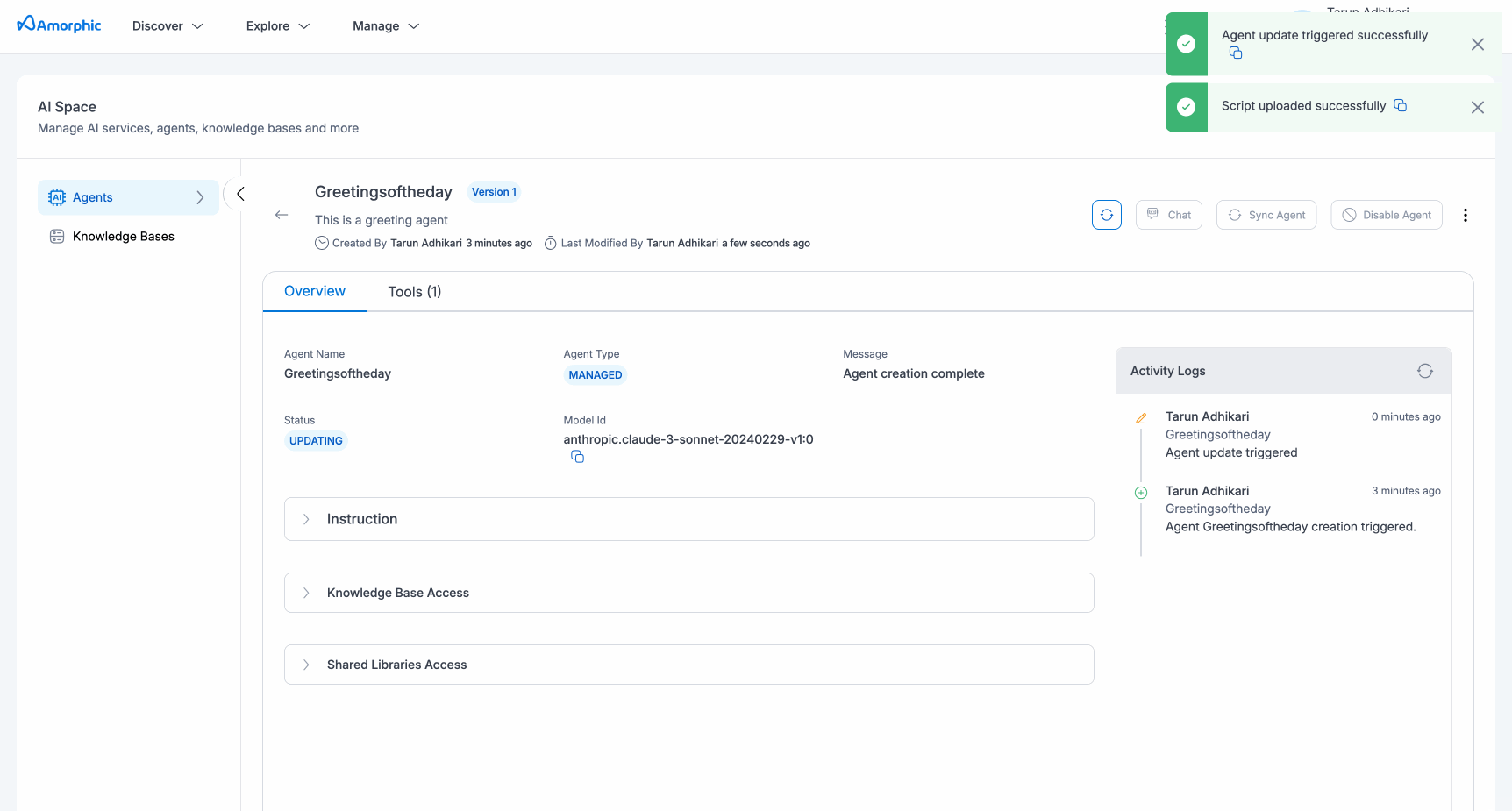
| Tool | Users must add at least one tool to proceed from this section. This tool will be available to the agent for consumption to solve the user's problem. It takes the following parameters:
|
| Script | Users need to provide an agent script which the agent will be able to use and will contain all aforementioned tool definition/functionality. Users can either upload the script or write it. |
| Shared Libraries | User-accessible shared Libraries will be displayed. Users can attach these libraries to the agent for script utilities. |
| Knowledge Bases | User-accessible knowledge bases can also be attached to the agent for additional context and improved response generation. |
| Guardrails | User-accessible guardrails can also be attached to the agent for validating model responses against security rules defined by the user/system. |
- Click Create
- Agent creation takes a few minutes. The status will change from "CREATING" to "READY" when complete.
- In case the agent is not innately able to process the request, it may prompt the user to enter the parameter value which is not found.
- For tool parameters, the supported types are:
- Integer
- String
- Boolean
- Array
View Agent
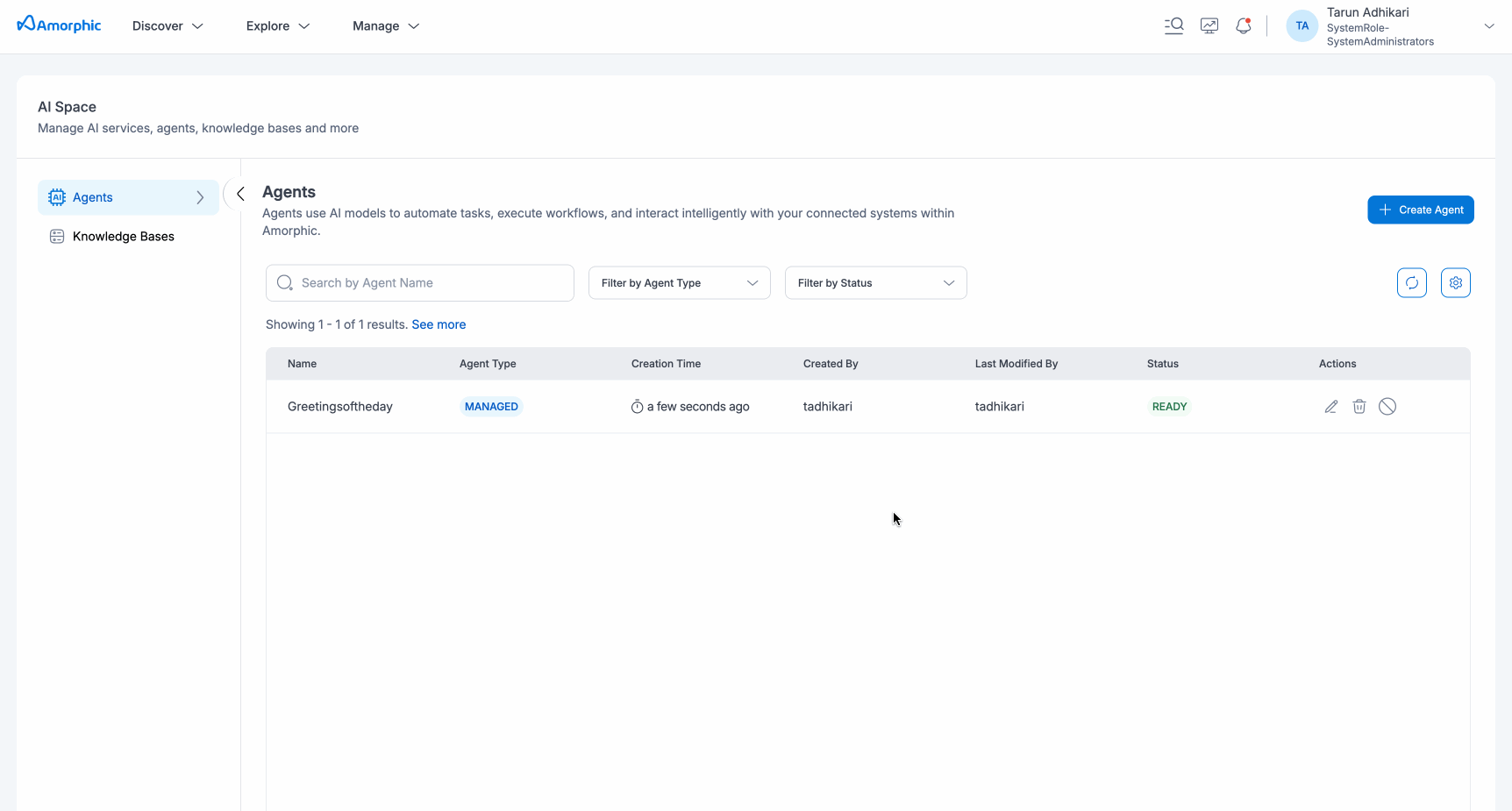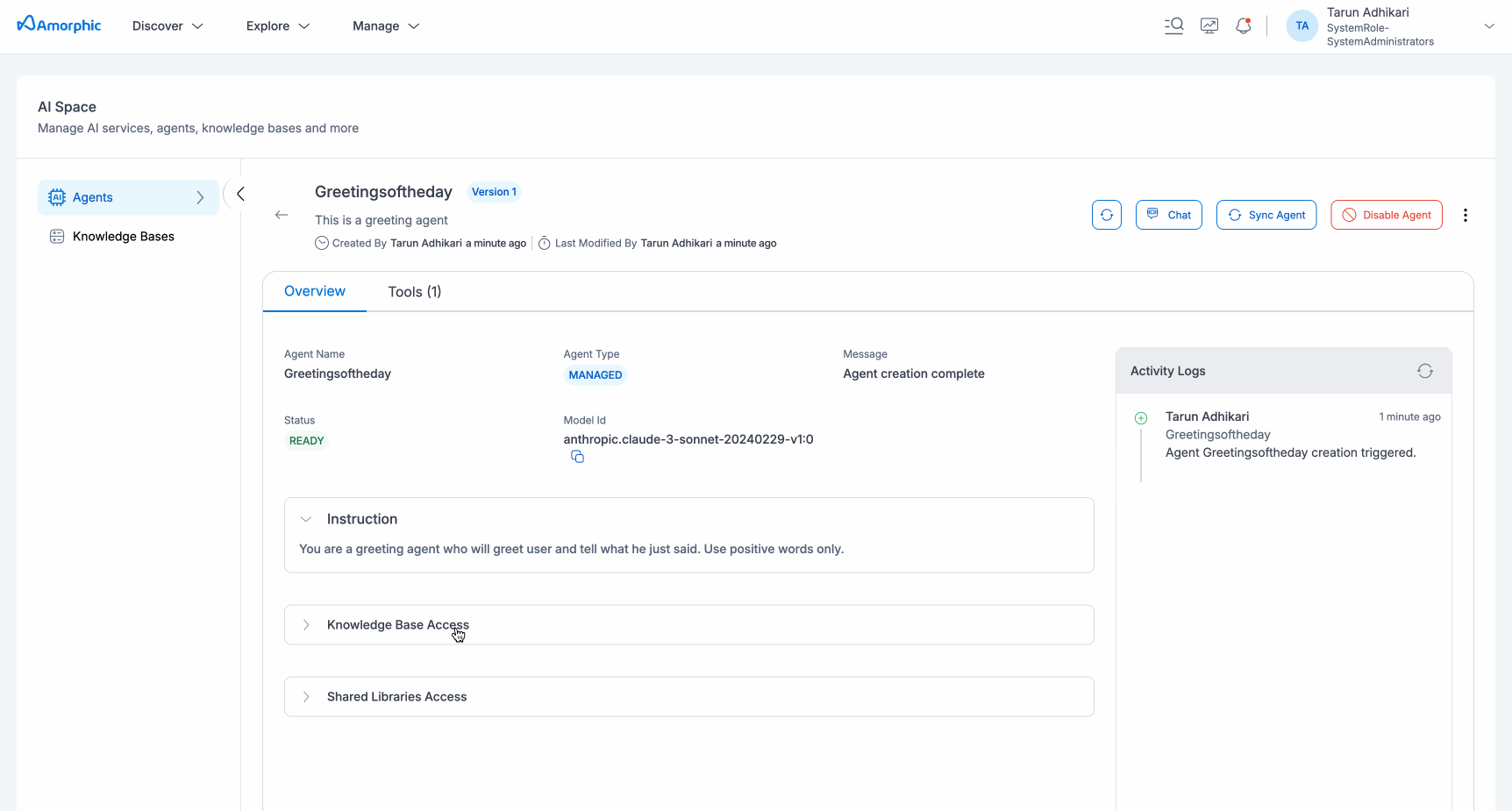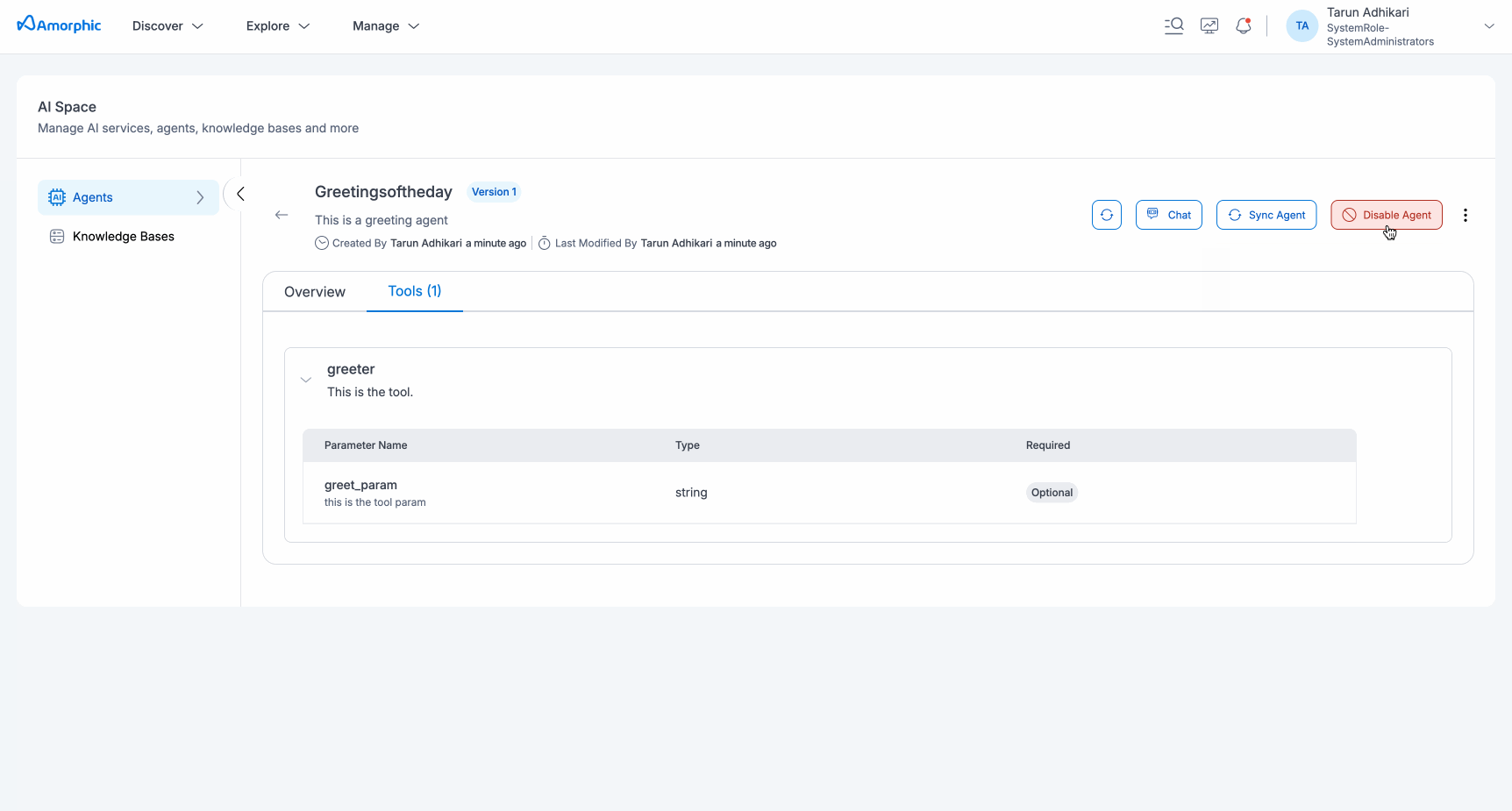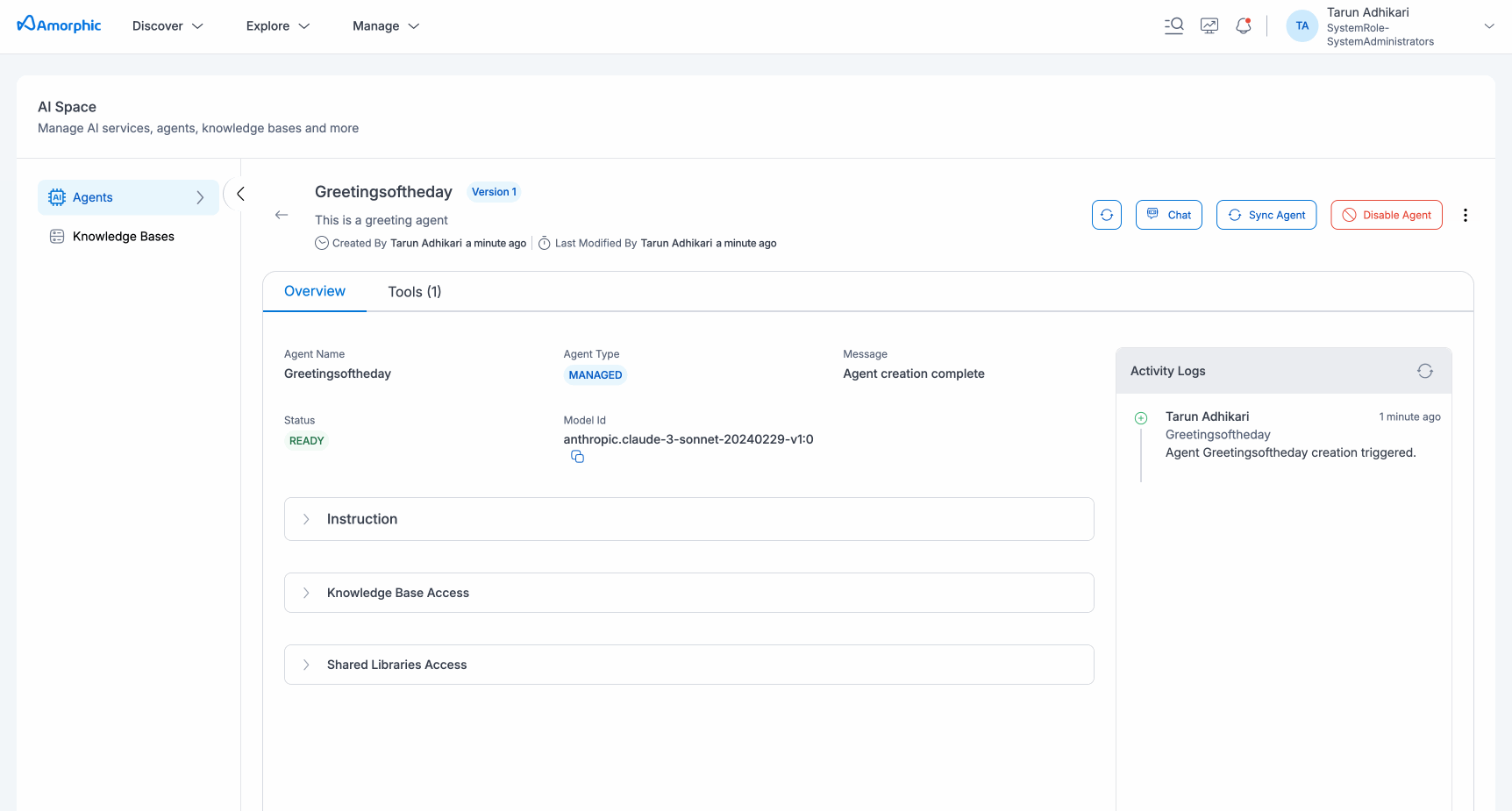
Click on any agent to see the agent's detail page. This page will show all of the configurations (such as Instructions, Shared Libraries, Knowledge Bases and Guardrail access metadata, etc.) done for the agent during create or update operations. This page will allow users to
- Access the Chat interface to utilize the agent.
- Tools tab will display all attached tools to the agent.
- Sync Agent functionality is available for users having attached knowledge base to the agent to sync it up with up-to-date data.
- Disable Agent to disable the agent for consumption.
Agents have different states:
- READY: Agent is active and ready to use
- CREATING: Agent is being set up
- UPDATING: Agent is being modified
- DELETING: Agent is being removed
- FAILED: Something went wrong
During these state transition avoid performing other actions on the agent.
Edit Agent
Users can edit the agent to update any existing metadata like instructions, model used, tools (new or updating old ones), etc. To update the agent, users can navigate to the edit agent options via the three dots option in the top corner of the agent details page.
Connecting Resources
Shared Libraries
Add custom Python libraries to your agent:
- Select from available shared libraries
- Libraries are automatically bundled for your agent
- Maximum 250MB per agent
Knowledge Bases
Connect up to 2 knowledge bases:
- Choose knowledge bases from the dropdown
- Agent will access information from these sources
- Permissions are automatically validated
Guardrails
Attach a guardrail to your agent:
- Choose a guardrail from the dropdown. This list contains user-created guardrails as well as the system defined ones.
- Agent responses will be validated against the guardrail attached.
- Permissions are automatically validated.
It is mandated that every agent should be attached with a guardrail to ensure governance over model responses. If the user does not provide any specific guardrail, the system will pick one of the system-defined guardrails and attach it to the agent by default.
Agent Scripts
When user tries to create/update an agent, the script can be uploaded or written in the Script Editor panel of the create/edit form. This script will contain the custom logic to do the tool invocation operations which will be chosen by the agent based on the use case. For create purposes, some templates are also provided to give end user idea about how elementary tools can be written.
Agent Logs
Agent logs can be accessed under the Logs Panel under more options(Three dots on top corner) on agent details page.
Operations
Generate Logs:
Used to process logs and store them into an S3 bucket for downloading later. To generate logs, user can go to the Logs Panel under more options(Three dots on top corner) on agent details page.
- Select a date range(optional)
- Click on Generate logs
View Logs
See logs for a given time range. To see what your agent is doing:
- Specify a time range (optional)
- Click View Logs
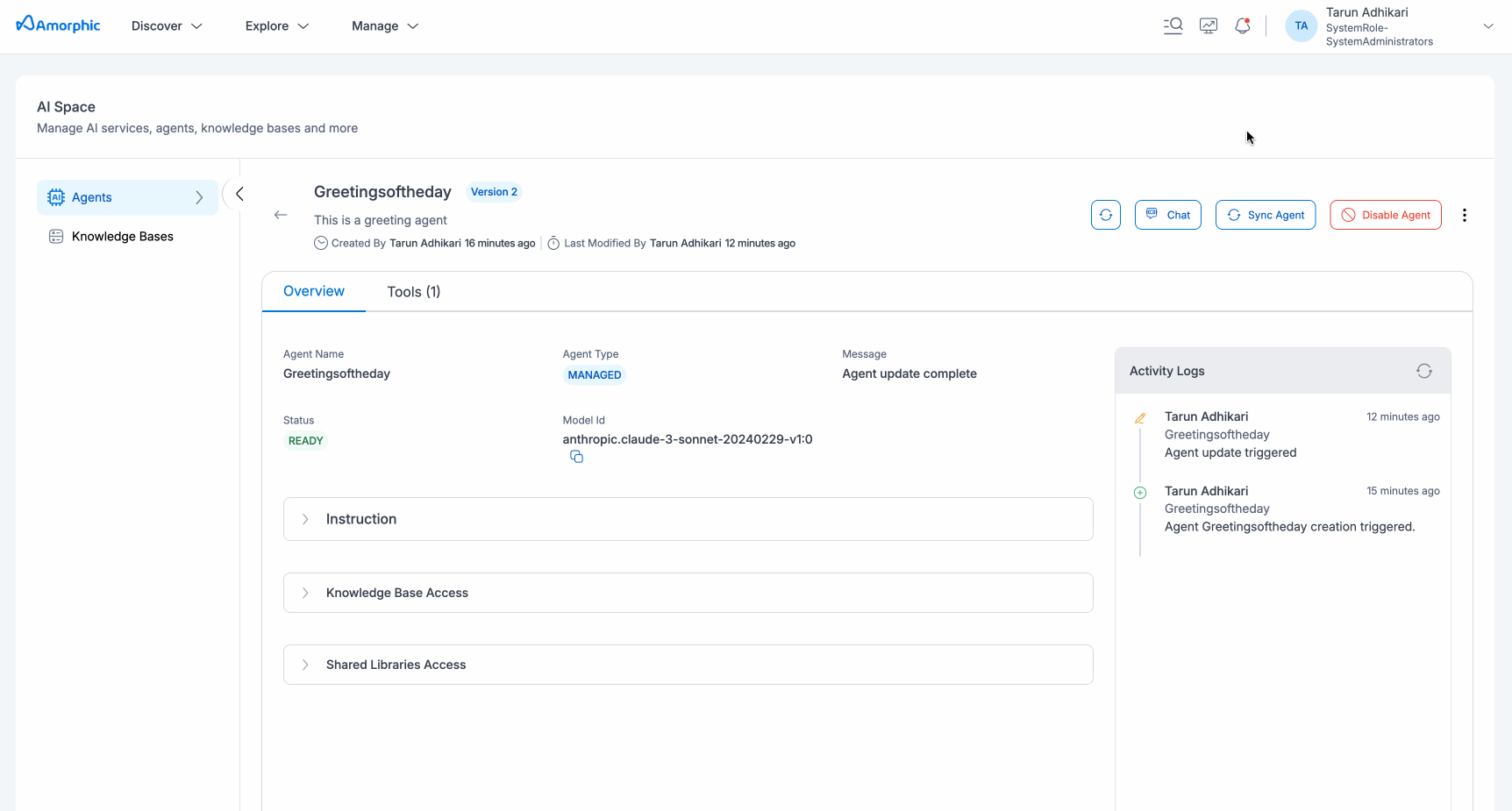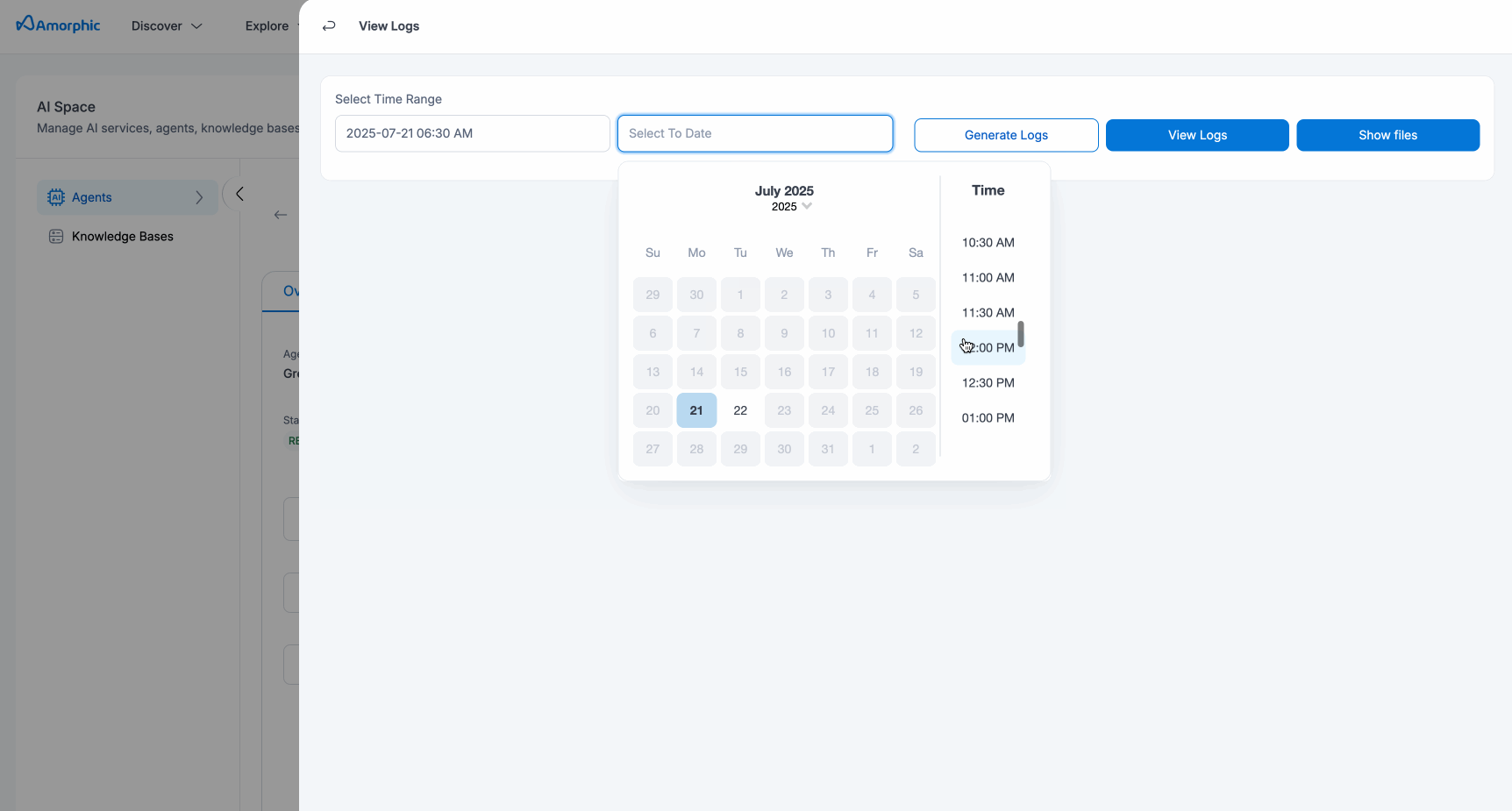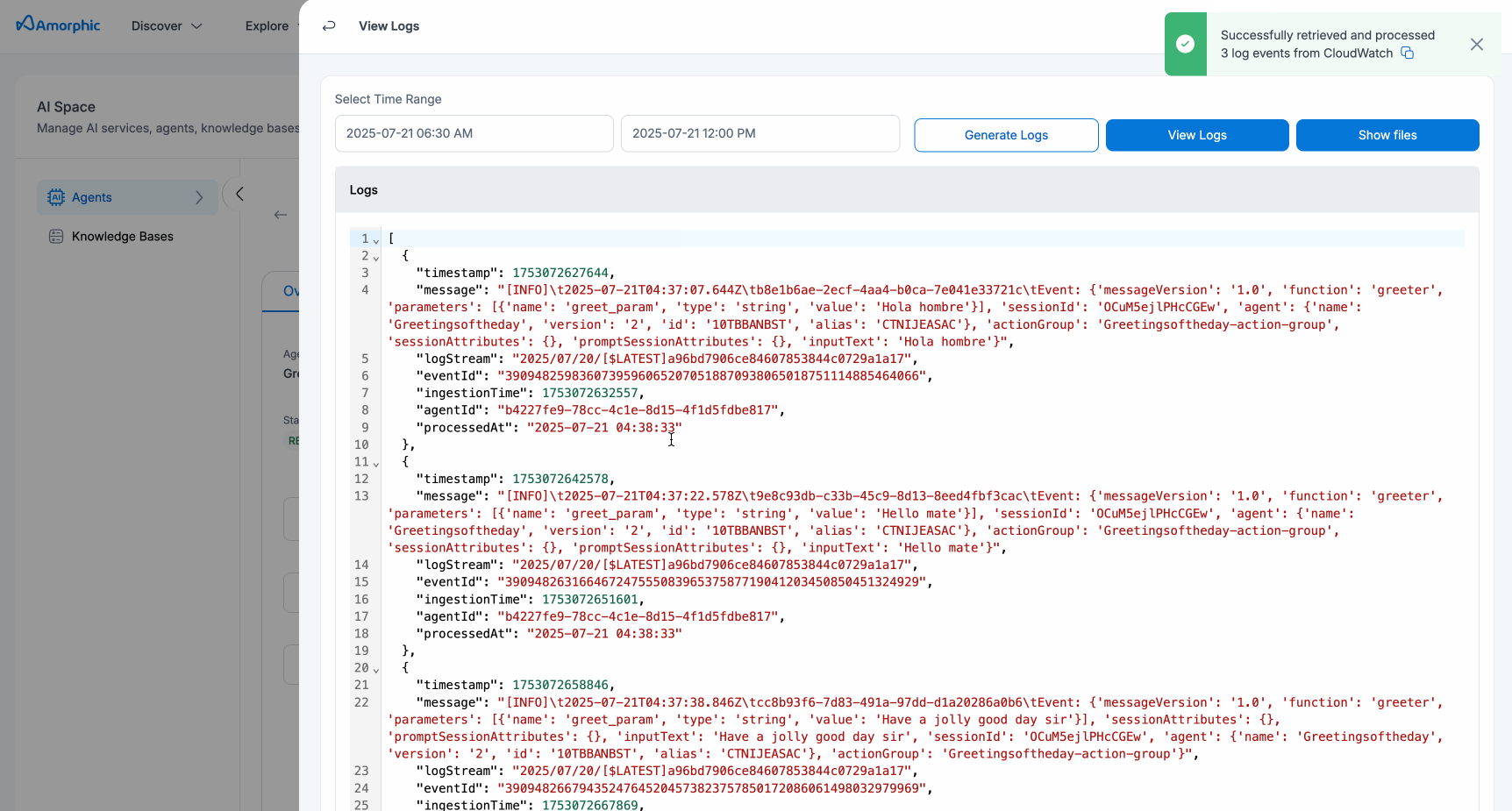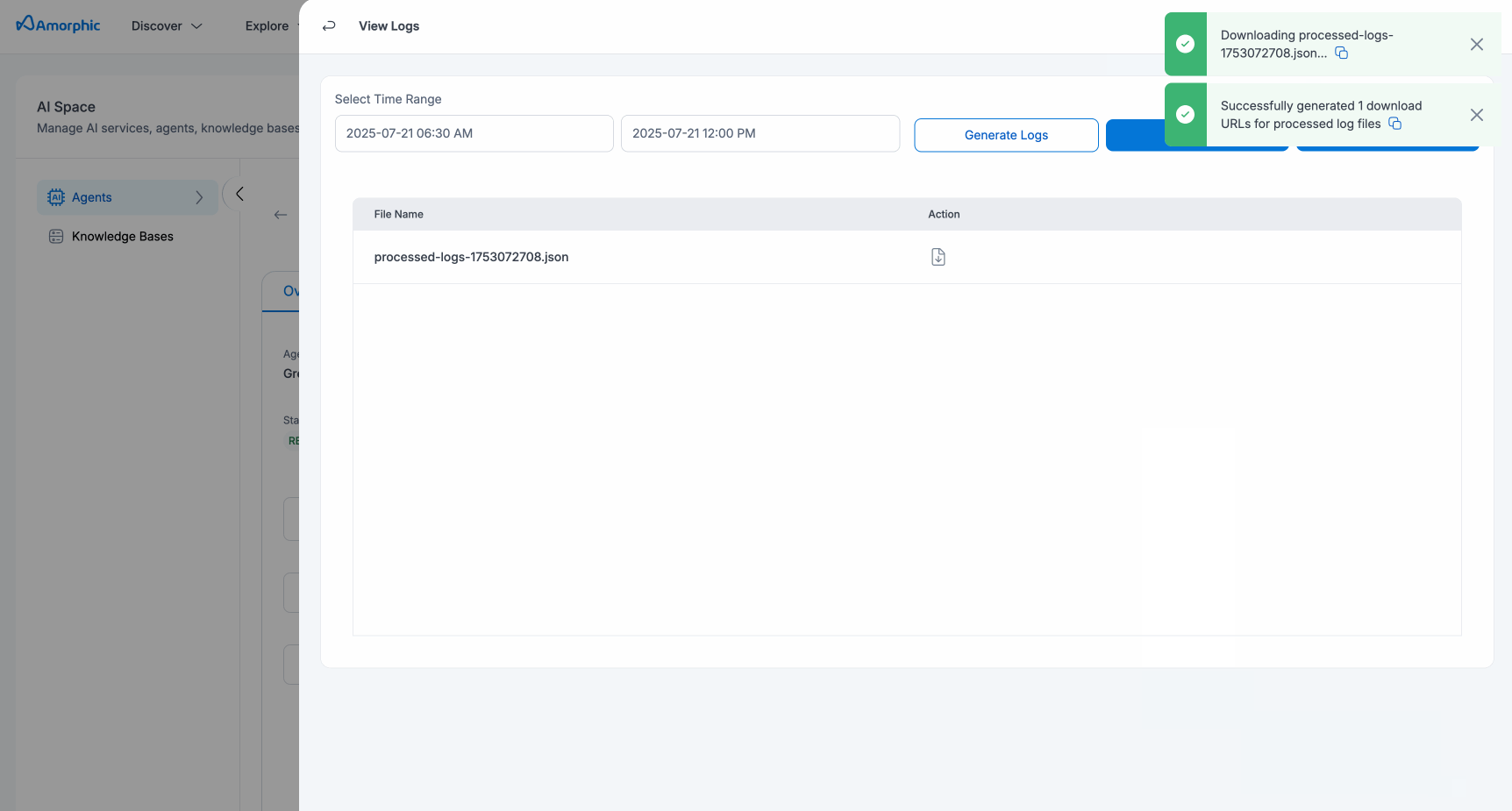
- Logs will appear for tool executions and actions performed using the agent script.
Download Logs
User can export processed logs:
- Specify a time range (optional)
- Click View Logs
- Any generated logs for the time range will be presented to user with download links.
Users need to add logging statements to their agent scripts to fully utilize this functionality as it provides the flexibility to debug issues based on preferences or identify tool invocations.
Common Use Cases
Customer Service Bot
Create an agent that handles customer inquiries:
- Connect to your knowledge base
- Add tools for ticket creation
- Configure responses for common questions
Data Analysis Assistant
Build an agent that analyzes data:
- Connect to your datasets
- Add analysis tools
- Generate insights and reports
Document Processor
Create an agent that processes documents:
- Add file upload tools
- Connect to document storage
- Extract and summarize information
Code Assistant
Build an agent that helps with coding:
- Add code generation tools
- Connect to development resources
- Provide debugging assistance
System Agents
Amorphic also provides a carefully curated set of pre-baked agents for users to play around with their application data. These agents are completely managed by the system; users will not be able to do any operations (edit/delete/sync/disable/share) on top of them and are by default shared with every user in the system with view permissions in the AI space. However they can interact with these agents and perform tasks.
Currently there are three System Agents that are readily available out of the box :
- Datalabeller Agent
- Summarizer Agent
- Error Diagnosis Agent
System Agents can be found under the agents listing page.
Datalabeller Agent
This System Agent is designed to perform data labelling tasks on top of user data. Datalabeller agent strictly works with unstructured data, and can work with files stored under user datasets as well as user provided custom data. The following are its capabilities :
- Label files in a dataset
- Label user provided text passages
- Approve/reject AI generated labels
- List files in a dataset
User-approved labels for a dataset file are stored under the Keywords section of the dataset for better searchability from Catalog. Users can come here any time and remove the approved labels at their will.
Summarizer Agent
This System Agent is designed to perform summarization tasks on top of user data. Summarizer agent can also work with files stored under user datasets as well as user provided custom data. The following are its capabilities :
- Summarize files in a dataset
- Summarize user provided text passages
- List files in a dataset
For Datalabeller and Summarizer agents, it is also required that models need to be configured for the Datasets configuration. For more details, refer to the Assign Models documentation.
Error Diagnosis Agent
The Error Diagnosis System Agent is primarily designed to carry out diagnosis of failed ETL job executions. This agent can provide a quick diagnosis as well as trigger the generation of a detailed error diagnosis report for an execution. The following are its capabilities :
- Explain the purpose and details of a job
- Diagnose errors in job executions
- Generate detailed diagnosis reports
- List previous job executions
For Error Diagnosis agent, it is also required that models need to be configured for the Jobs configuration. For more details, refer to the Assign Models documentation.
System Agents are system-defined agents built on top of models that are decided entirely by the system, taking model performance and other factors into consideration.
Due to this, certain system agents may not be available since they're powered by models that may not be accessible (or supported for cross-region inference) in the region where your Amorphic application is deployed.